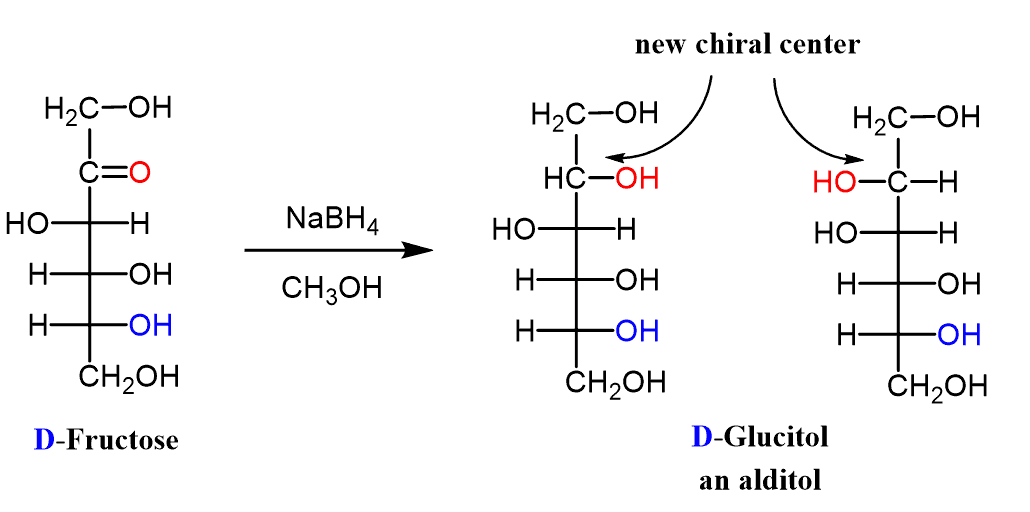
The carbonyl group in aldoses and ketoses can be reduced by NaBH4 to a 1o and 2o alcohol respectively. The product of this reaction is a polyalcohol called an alditol.

The reduction of the ketoses creates a new chiral center in both configurations. This is because the carbonyl group is transformed into a secondary alcohol while in the case of aldoses, it forms a primary alcohol which is not chiral.
Remember also that cyclic hemiacetals are always in equilibrium with the open-chain form and therefore, they can also be reduced to alditols.
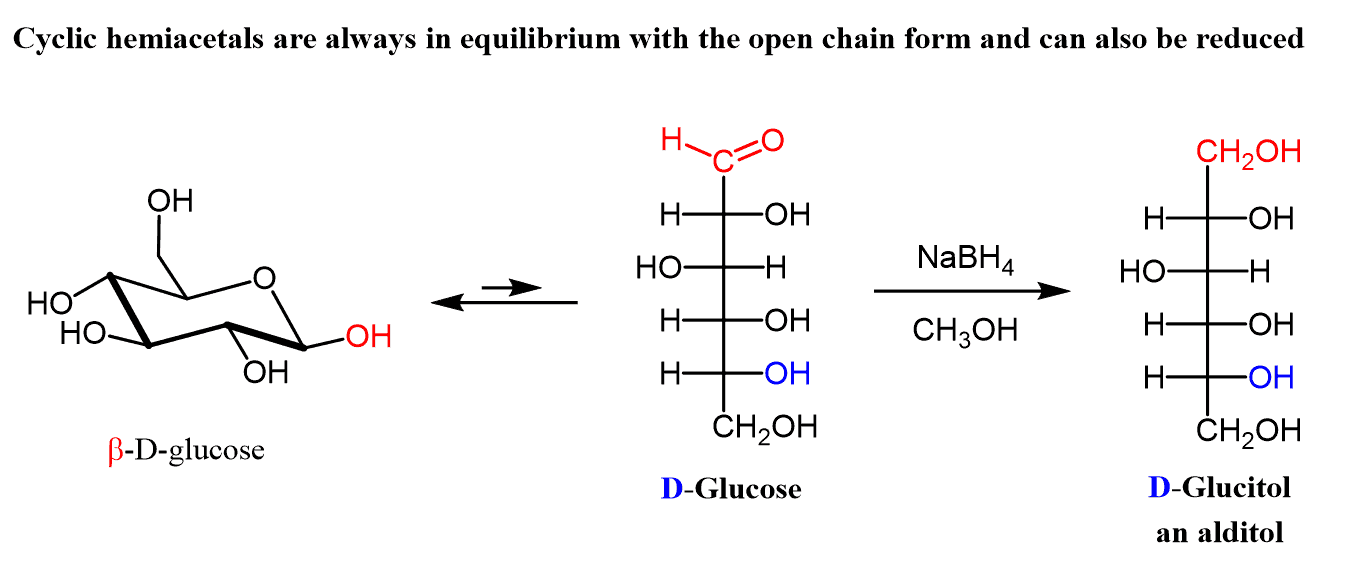
Even though the open-chain form exists in small quantities, the reduction product shifts the equilibrium to right forming more of it as the reaction proceeds.
Need some practice on carbohydrates?
Check this Multiple-Choice, summary quiz on the structure and reactions of carbohydrates with a 40-min video solution!
Carbohydrates Practice Problem Quiz
Check also in Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates – Structure and Classification
- Erythro and Threo
- D and L Sugars
- Aldoses and Ketoses: Classification and Stereochemistry
- Epimers and Anomers
- Converting Fischer, Haworth, and Chair forms of Carbohydrates
- Mutarotation
- Glycosides
- Isomerization of Carbohydrates
- Ether and Ester Derivatives of Carbohydrates
- Oxidation of Monosaccharides
- Reduction of Monosaccharides
- Kiliani–Fischer Synthesis
- Wohl Degradation

