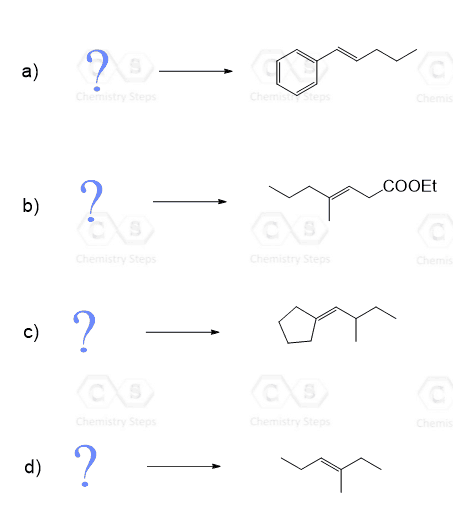
In the previous post, we discussed the principle and mechanism of the Wittig reaction.
Go over those if you need to, and in the following practice problem, we will work on proposing a synthesis for Wittig reagents as well as preparing alkenes using the Wittig reagent and alternative methods.
First, let’s make a plan for solving these problems.
Wittig Reaction – Solving Problems by Retrosynthetic Analysis
To predict the reactants of a Wittig reaction, cleave the C=C bond and place an oxygen on one end and (Ph)3P on the other end of the bond:
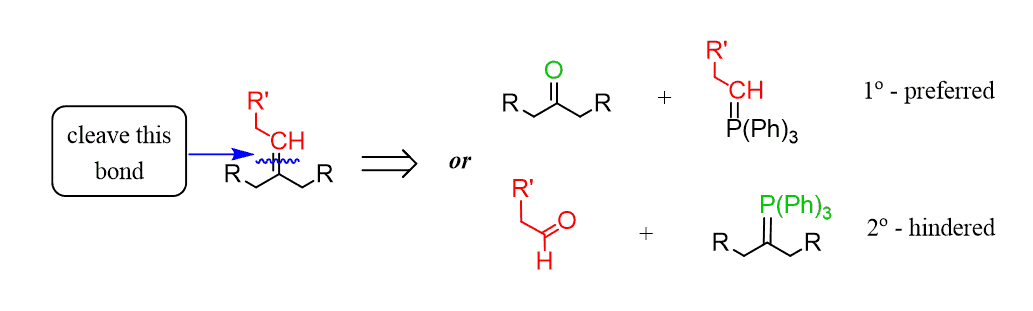
The arrow above shows the retrosynthetic direction – i.e., what compounds had reacted to prepare the alkene.
And you can see there might be two different combinations of reacting a carbonyl compound and a Wittig reagent to prepare the given alkene.
So, to determine the preferred route, keep in mind that the Wittig reagent is prepared by an SN2 reaction. Which means that a less substituted carbon connected to P(PH)3 is easier to prepare; therefore, it is the preferred route:
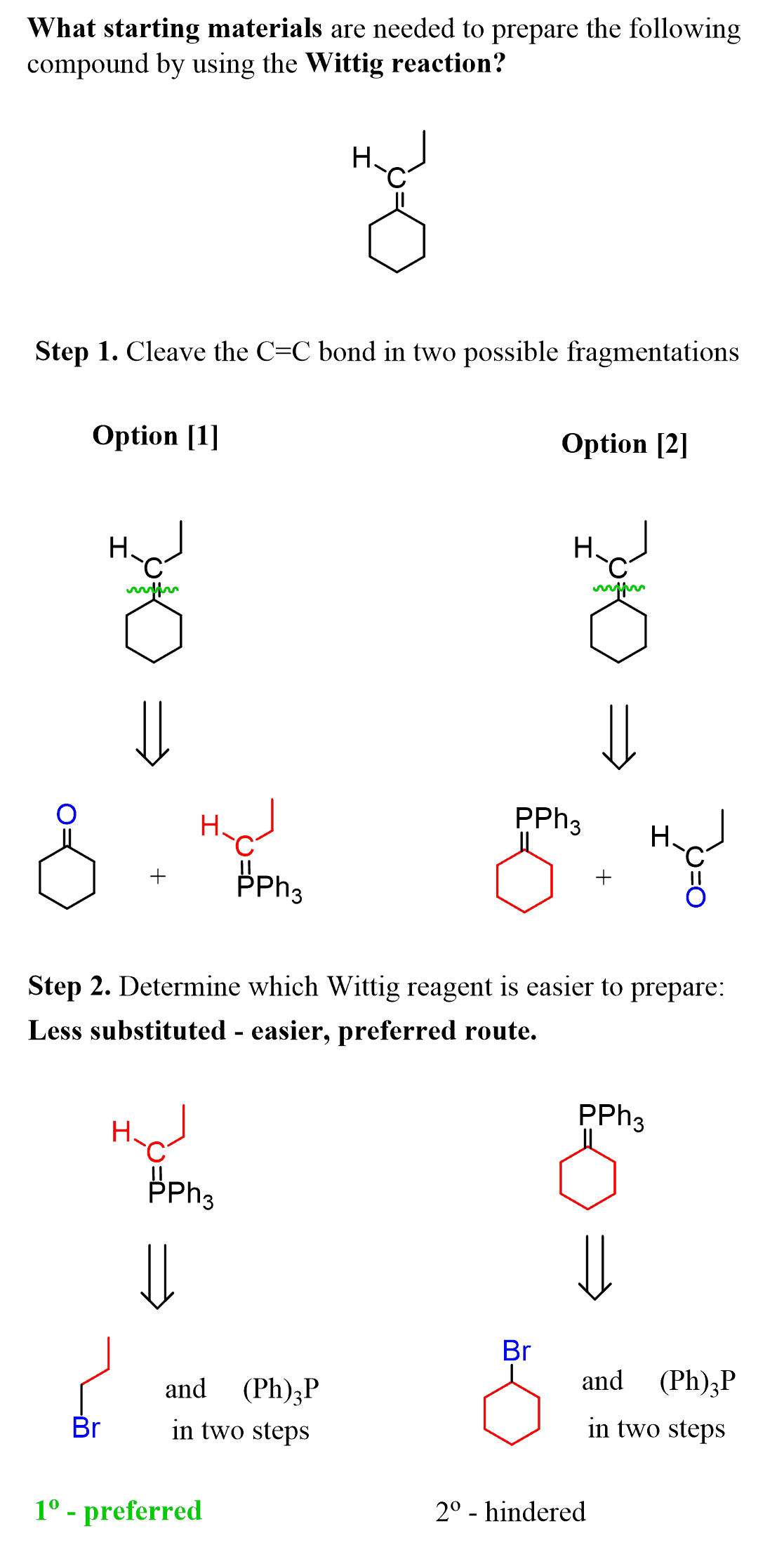
The 1-bromopropane in the first route will react more easily with PPh3 than the bromocyclohexane would, since we are comparing the reactivity of a primary and secondary substrate in SN2 reactions.
Therefore, the first option is a preferred way of performing the Wittig reaction.