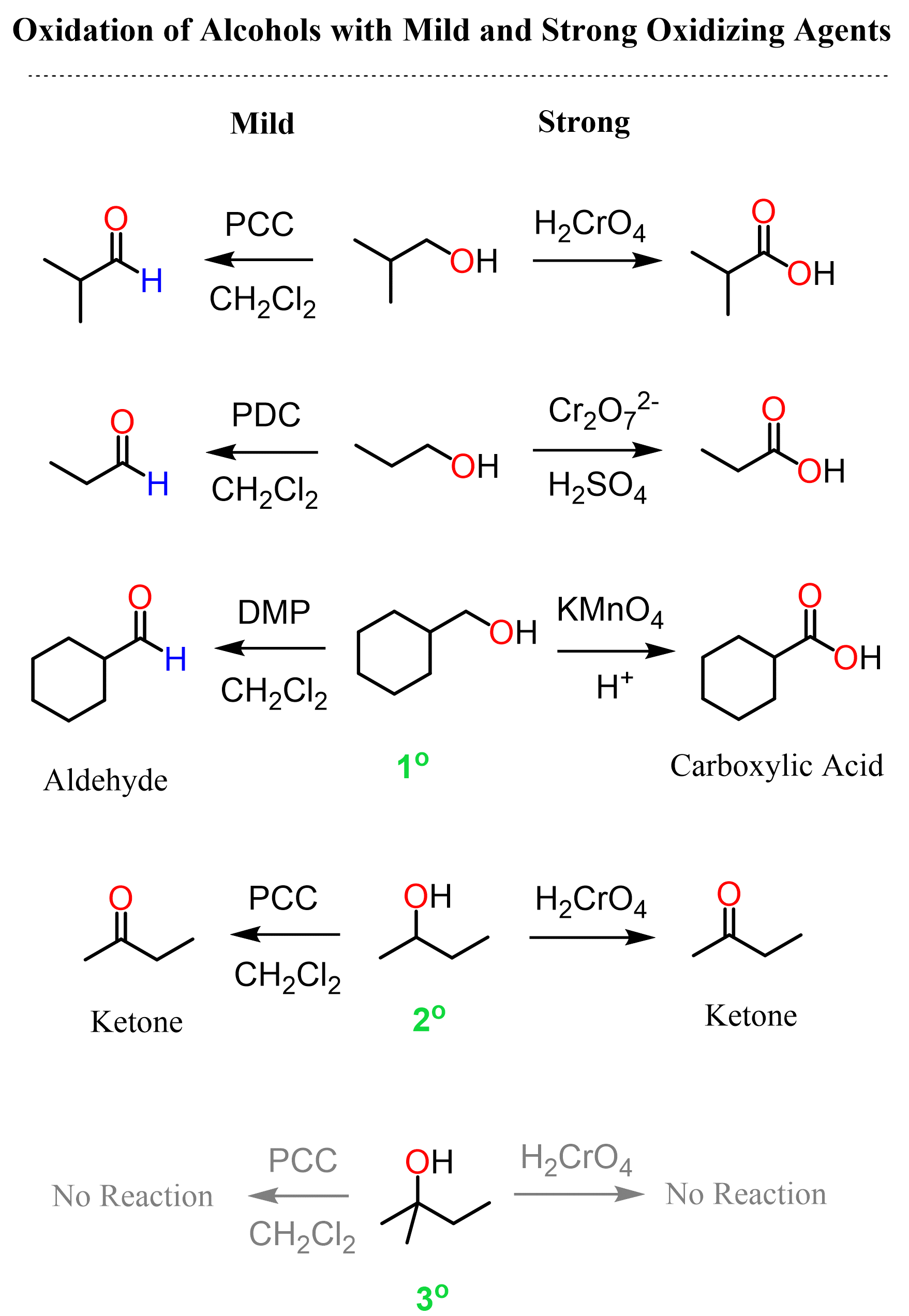
Alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and ketones using a variety of oxidizing agents. The outcome of the oxidation depends both on the oxidizing agent and the structure of the alcohol. Recall from the oxidation states of organic compounds that alcohols are below all the carbonyl compounds, and the aldehydes are between the alcohols and carboxylic acid derivatives:

So, to oxidize the alcohol to an aldehyde we need conditions that do not over oxidize it to a carboxylic acid. For this, we have what’s called mild oxidizing agents. The most common mild oxidizing agents are pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), pyridinium dichromate (PDC), Swern oxidation using DMSO, (COCl)2 and Et3N, and the Dess-Martin (DMP) oxidation:

Strong oxidizing agents such as Jones reagent convert primary alcohols to carboxylic acids. On the other hand, secondary alcohols are always oxidized to ketones, whereas tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized to any carbonyl as their structure simply does not allow this transformation.
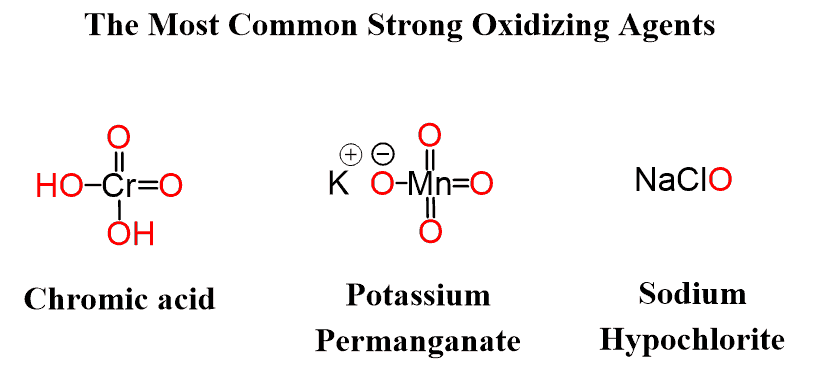
These are the most common strong oxidizing agents you will need to know:
Here are some examples of mild oxidizing agents converting primary alcohols to aldehydes:
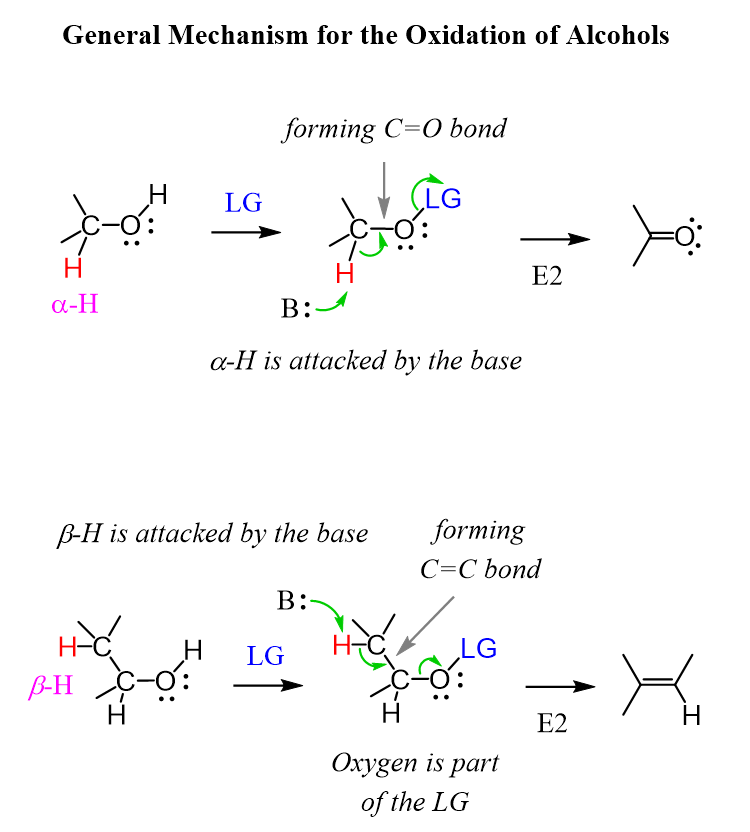
All the oxidation reactions of alcohols work based on the same principle of converting the OH into a good leaving group and eliminating the adjacent hydrogen to form a C=O double bond. It is essentially a type of an E2 reaction but instead of a C=C double bond, we are forming a C=O double bond.
This article is a summary of the patterns of oxidizing primary a secondary alcohols using different strong and mild oxidizing agents. We have a separate post with mechanistic details of all the oxidizing agents mentioned here, so feel free to check that out as well.

Check Also
- Nomenclature of Alcohols: Naming Alcohols based on IUPAC Rules with Practice Problems
- Preparation of Alcohols via Substitution or Addition Reactions
- Reaction of Alcohols with HCl, HBr, and HI Acids
- Mesylates and Tosylates as Good Leaving Groups
- SOCl2 and PBr3 for Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- Alcohols in Substitution Reactions Practice Problems
- POCl3 for Dehydration of Alcohols
- Dehydration of Alcohols by E1 and E2 Elimination
- The Oxidation States of Organic Compounds
- LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism
- Alcohols from Carbonyl Reductions – Practice Problems
- Grignard Reaction in Preparing Alcohols with Practice Problems
- Grignard Reaction in Organic Synthesis with Practice Problems
- Protecting Groups For Alcohols in Organic Synthesis
- Oxidation of Alcohols: PCC, PDC, CrO3, DMP, Swern and All of That
- Diols: Nomenclature, Preparation, and Reactions
- NaIO4 Oxidative Cleavage of Diols
- The Pinacol Rearrangement
- The Williamson Ether Synthesis
- Alcohol Reactions Practice Problems
- Naming Thiols and Sulfides
- Reactions of Thiols
- Alcohols Quiz – Naming, Preparation, and Reactions
