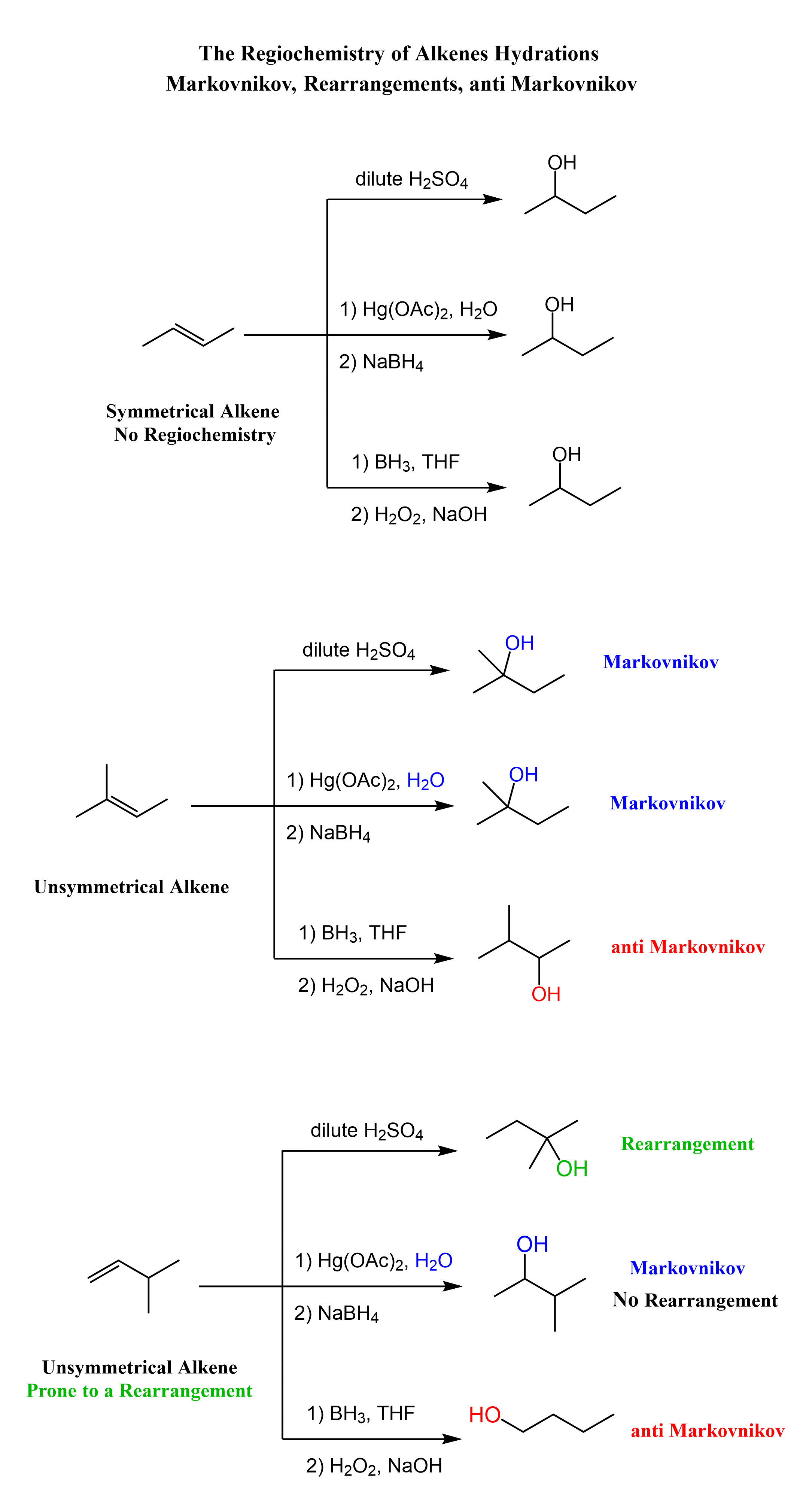
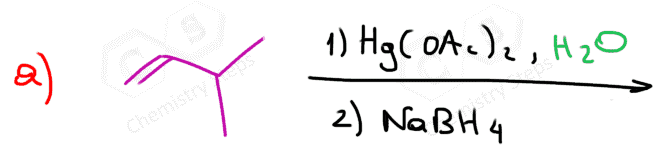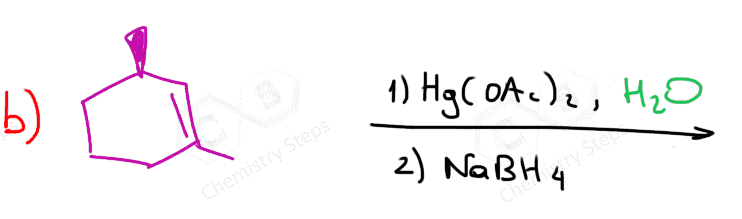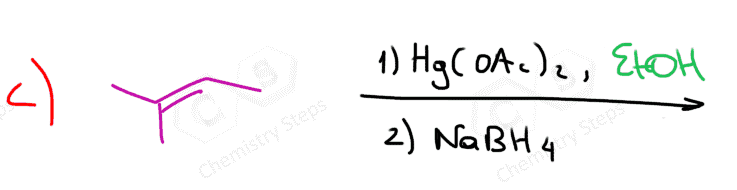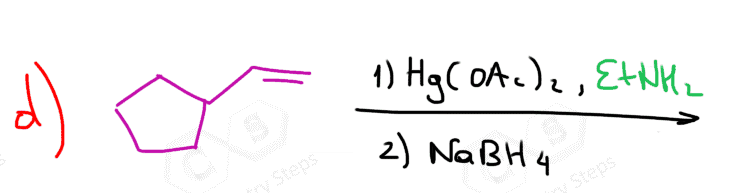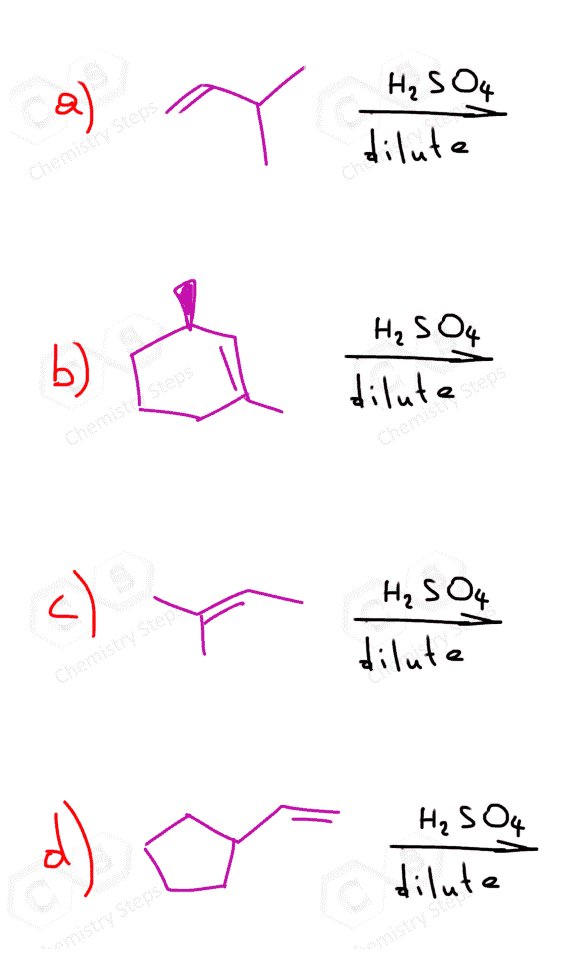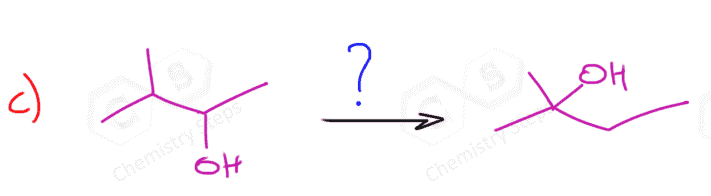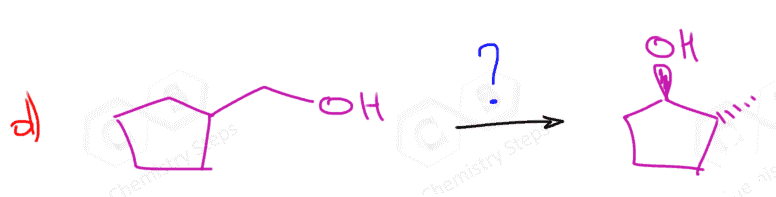The addition reactions of water to alkenes (hydration of alkenes) can be viewed as adding an H and OH groups to the double bond. There are a few ways of achieving this, and the key difference is the regiochemical outcome of the reaction. More specifically, depending what reagent we use, the addition to water can be in Markovnikov or anti-Markovnikov fashion:
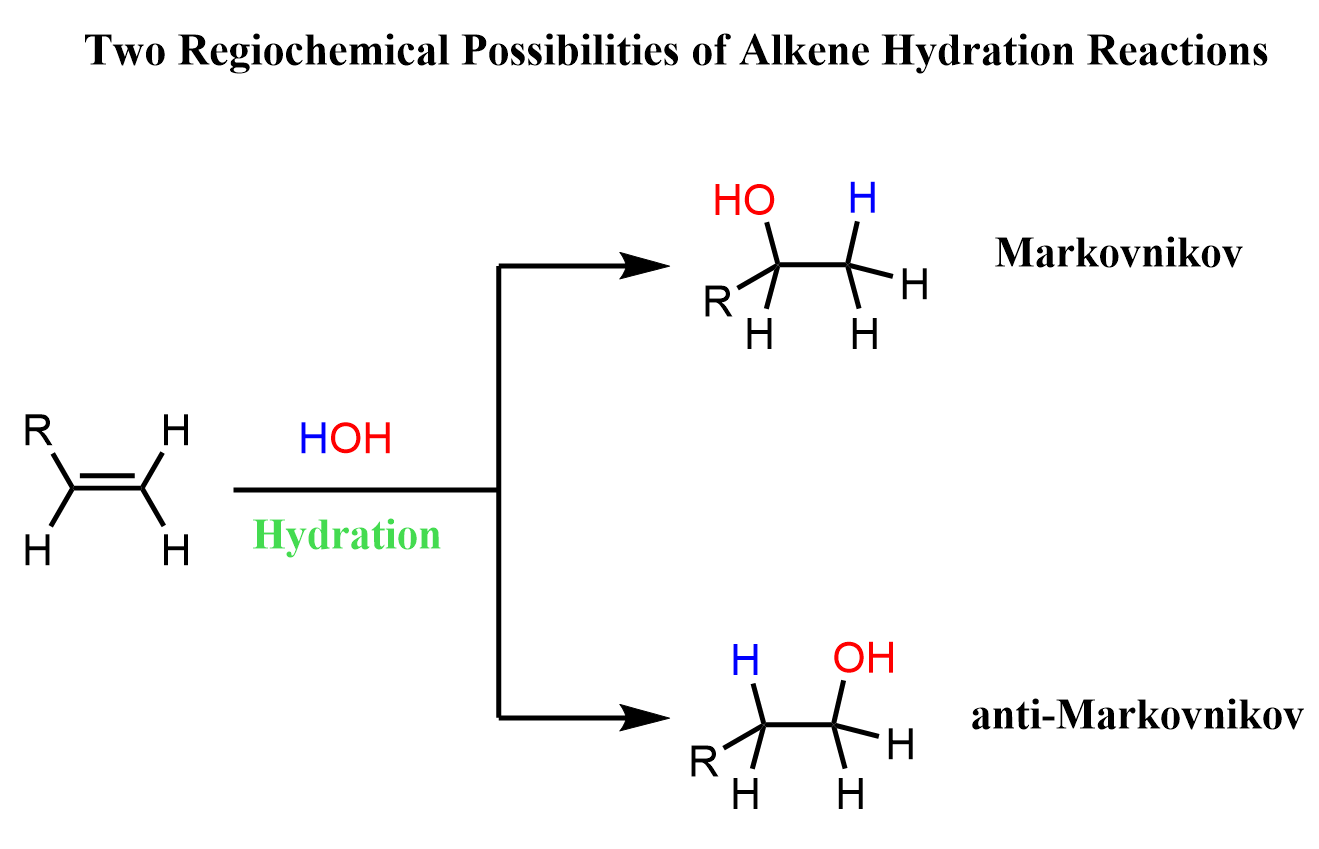
A reminder that Markovnikov’s rule is followed when the X component of the HX reactant (for example HCl, HBr, HI, HOH) adds to the more substituted carbon atom.
Now that we know the hydration of alkanes is and what regiochemical outcomes are possible, let’s mention the methods used for each transformation. These are acid-catalyzed hydration and the hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes. The acid-catalyzed hydration is used for a Markovnikov addition of water, and hydroboration-oxidation is for the anti-Markovnikov addition:
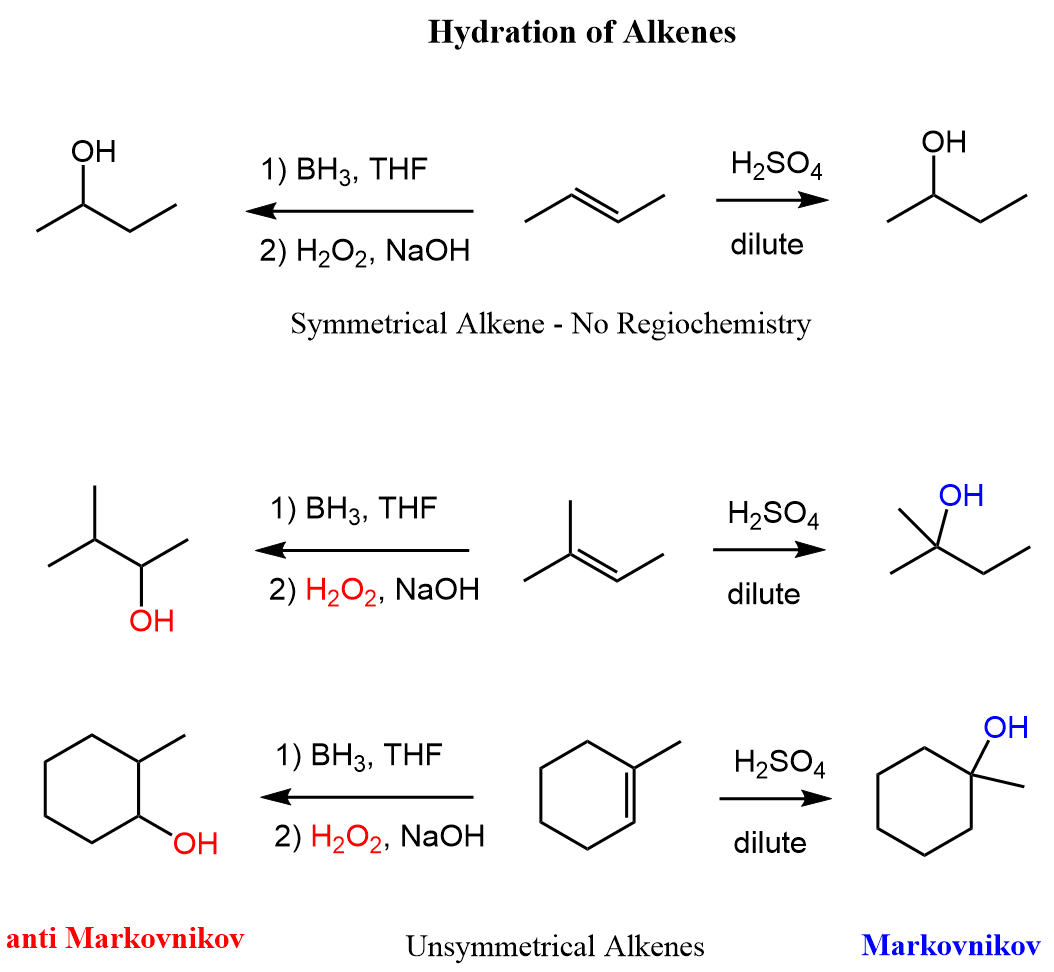
Notice that in the first reaction, we have a symmetrical alkene, and therefore the regiochemistry is irrelevant there and both methods give the same alcohol.
In the next part of this article, we will briefly discuss each of these methods for the hydration of unsymmetrical alkenes, and will also bring in the oxymercuration-demercuration reaction which is a useful alternative to the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes. You can check the linked articles in the text for more details about each of these reactions,
Markovnikov Addition of Water to Alkenes
The most common way of hydrating alkenes in Markovnikov fashion is the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes which adds the OH group to the more substituted carbon atom:

The Mechanism of Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Akenes
Let’s draw a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of but-1-ene to understand the regiochemistry of this hydration reaction. The reaction goes through a carbocation intermediate and out of two or more possibilities, the most stable one is formed. This is the more substituted carbocation because remember, their stability increases with the number of alkyl groups connected to the positively charged carbon atom:
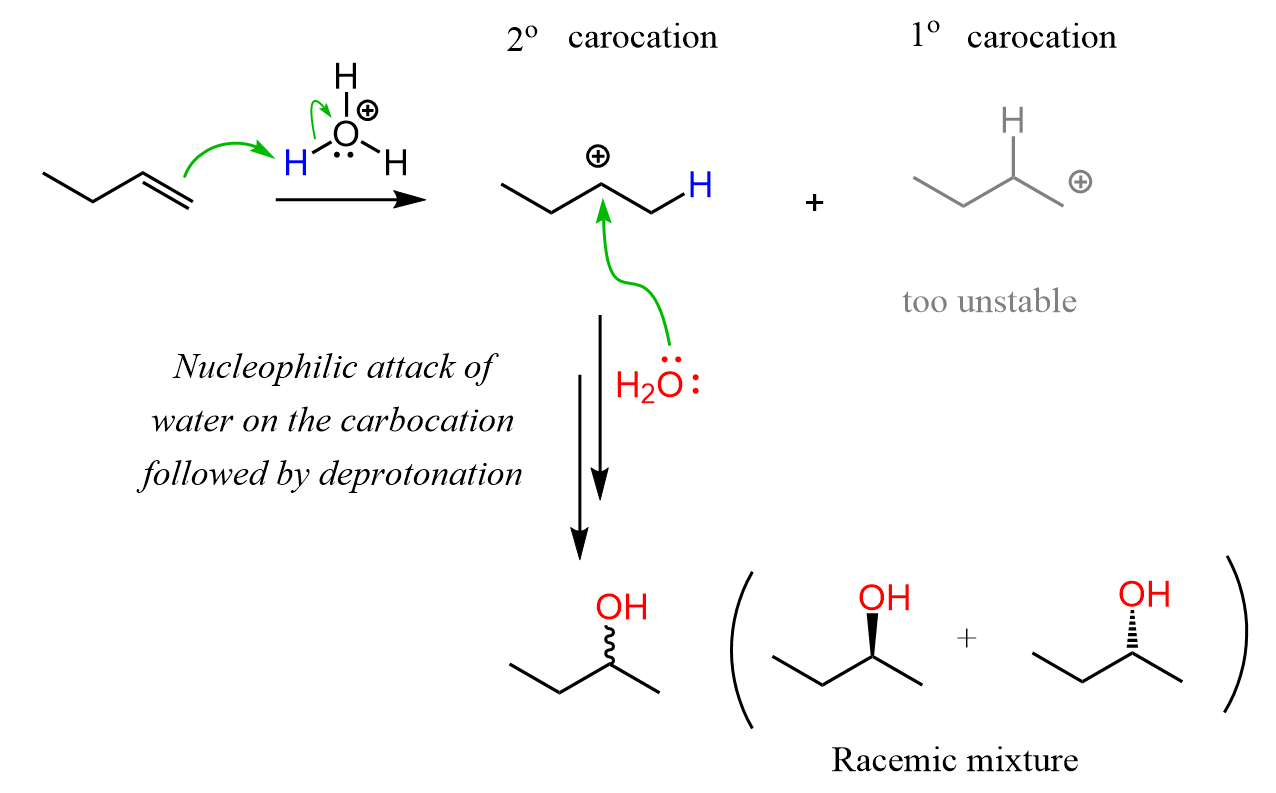
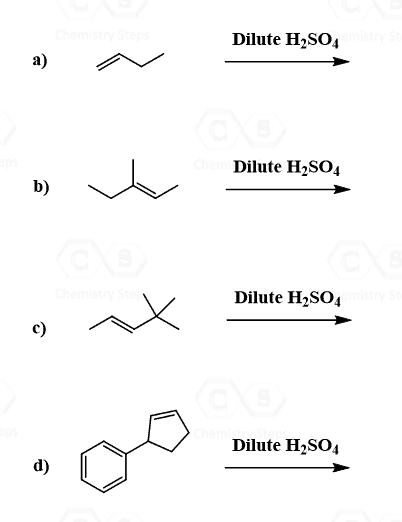
Because the reaction goes through a carbocation intermediate, and this should be a hint to you to watch out for possible rearrangements. Check out the post about rearrangements in addition reactions of alkenes. As we have seen in SN1 and E1 reactions, whenever possible carbocation intermediates will undergo a rearrangement to form the more stable analog.
Rearrangements in Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
In the example, we have shown above, there is no possibility of converting the secondary carbocation to a tertiary carbocation. Let’s consider addition of water to alkene going through a transformation of a secondary carbocation to a tertiary one:
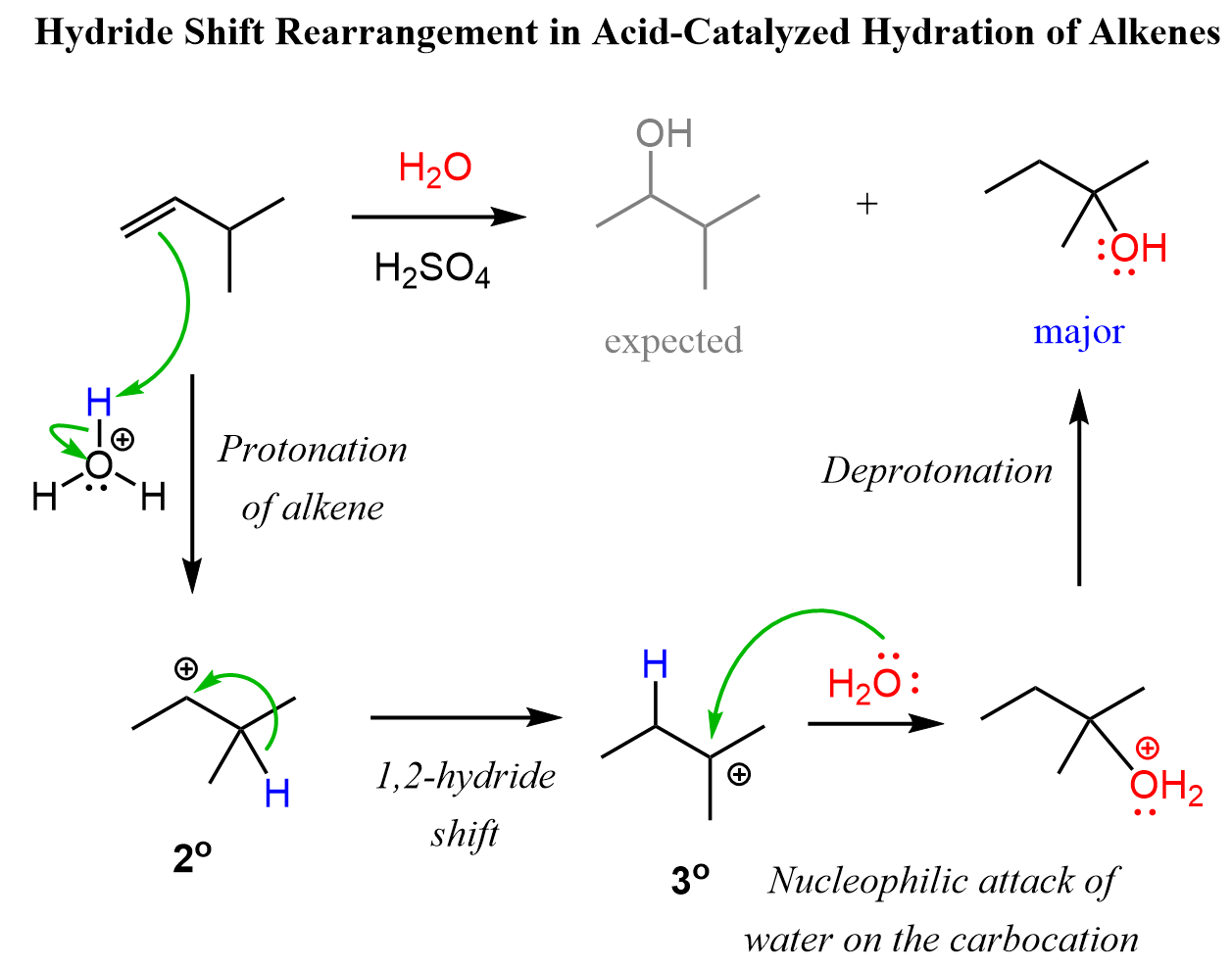
Methyl and ring expansion rearrangements are possible during the hydration and other electrophilic addition reactions to alkenes. More on the rearrangements in alkene addition reactions can be found here.
Oximercuration-Demercuration to Avoid Rearrangements
One way of avoiding a rearmament in the hydration of alkenes following the Markovikov’s rule is the use of mercury acetate (Hg(OAc)2). This is called the Oxymercuration-Demercuration reaction for the hydration of alkenes:

The key difference, compared to acid-catalyzed hydration, is that the intermediate in the oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is the mercurinium ion which does not undergo a rearrangement. What is also important is that the water attacks the more substituted carbon of the mercurinium ion, thus the corresponding alcohol is formed (Markovnikov addition):
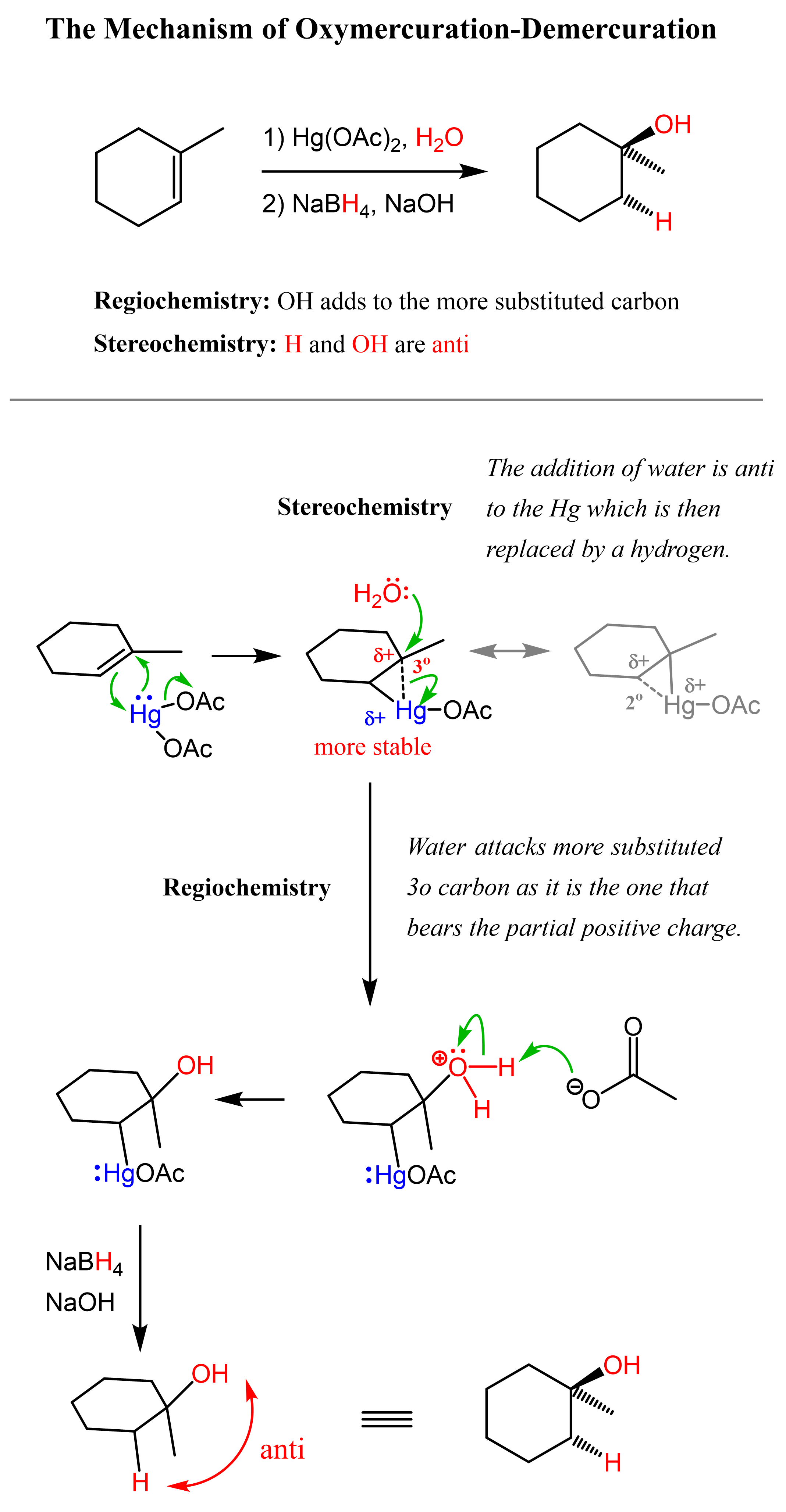
In the last part, the mercury is then removed using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) which reduces the acetoxymercury group and replaces it with its own hydrogens hydrogen. This is described as demercuration, and it is believed to be following a radical mechanism that is not covered in undergraduate courses.
The Stereochemistry of Acid-catalyzed hydration
As we see in the mechanism shown above, if acid-catalyzed hydration produces an alcohol with one chirality center, then the products will be a mixture of two enantiomers:

The reason for this is the formation of the carbocation intermediate which, due to the planar geometry, is attacked by water from both faces thus leading the equal amounts of the newly forming chirality center. If more than one chirality centers are present in the product, the corresponding diastereomers will also be formed. Check this article about the stereochemistry of alkene addition reactions for more details.
The Stereochemistry of Oxymercuration-Demercuration
In oxymercuration-demercuration, the H and OH are added to the opposite faces of the double bond. This is called anti addition. With this said, there is generally no control over which face of the double the OH and H are added unless there are some steric interactions preventing the addition from one of the sides. Therefore, chiral centers (if any) are formed in equal amounts and the product is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers.
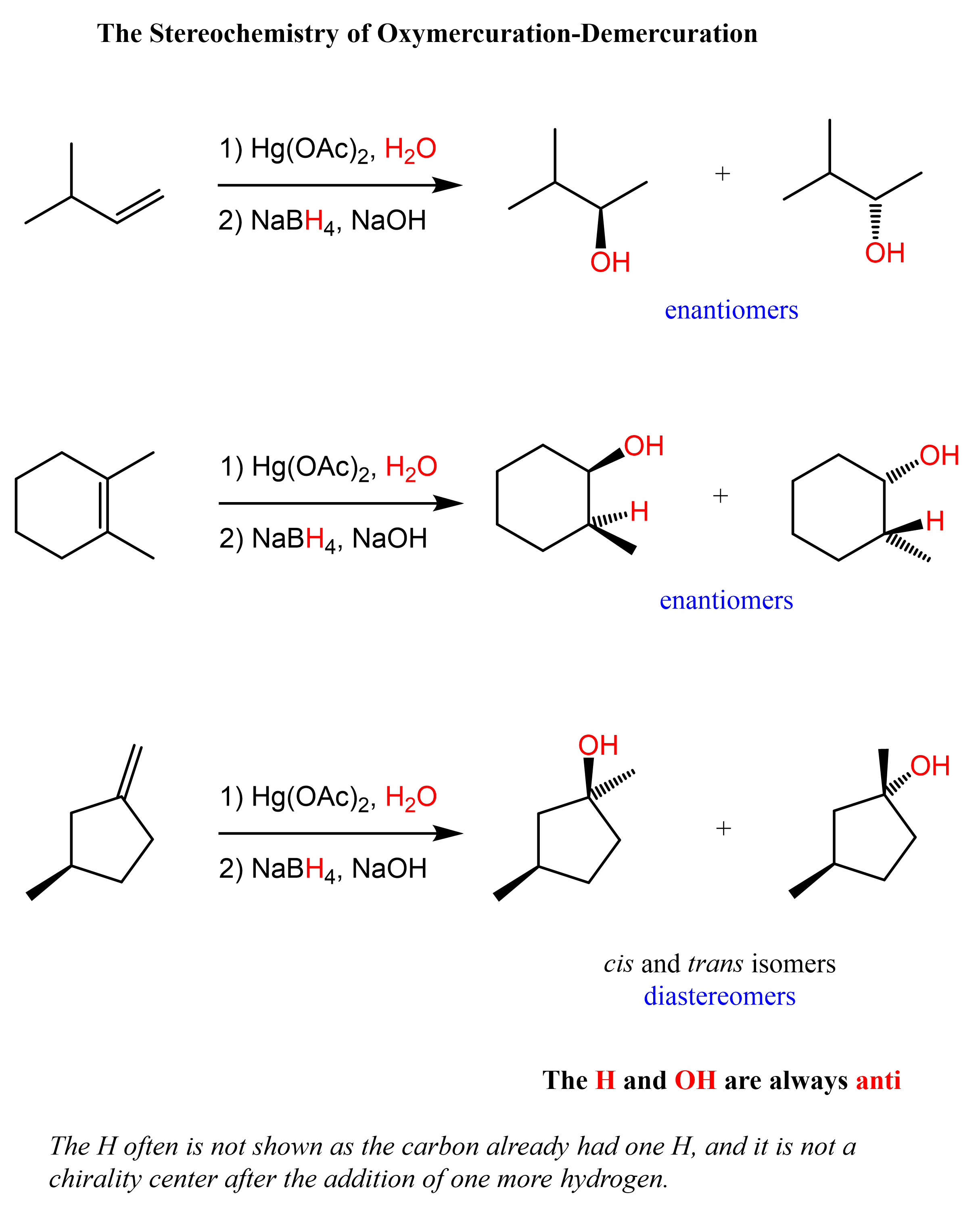
Notice from the last reaction that diastereomers can also be formed if the product contains two or more chirality centers.
This is because while the newly-forming centers are going to be R and S, the original chirality center is intact, thus the alcohols are not mirror images. Let’s also show the mechanism of how diastereomers can form in oxymercuration-demarcation relations:
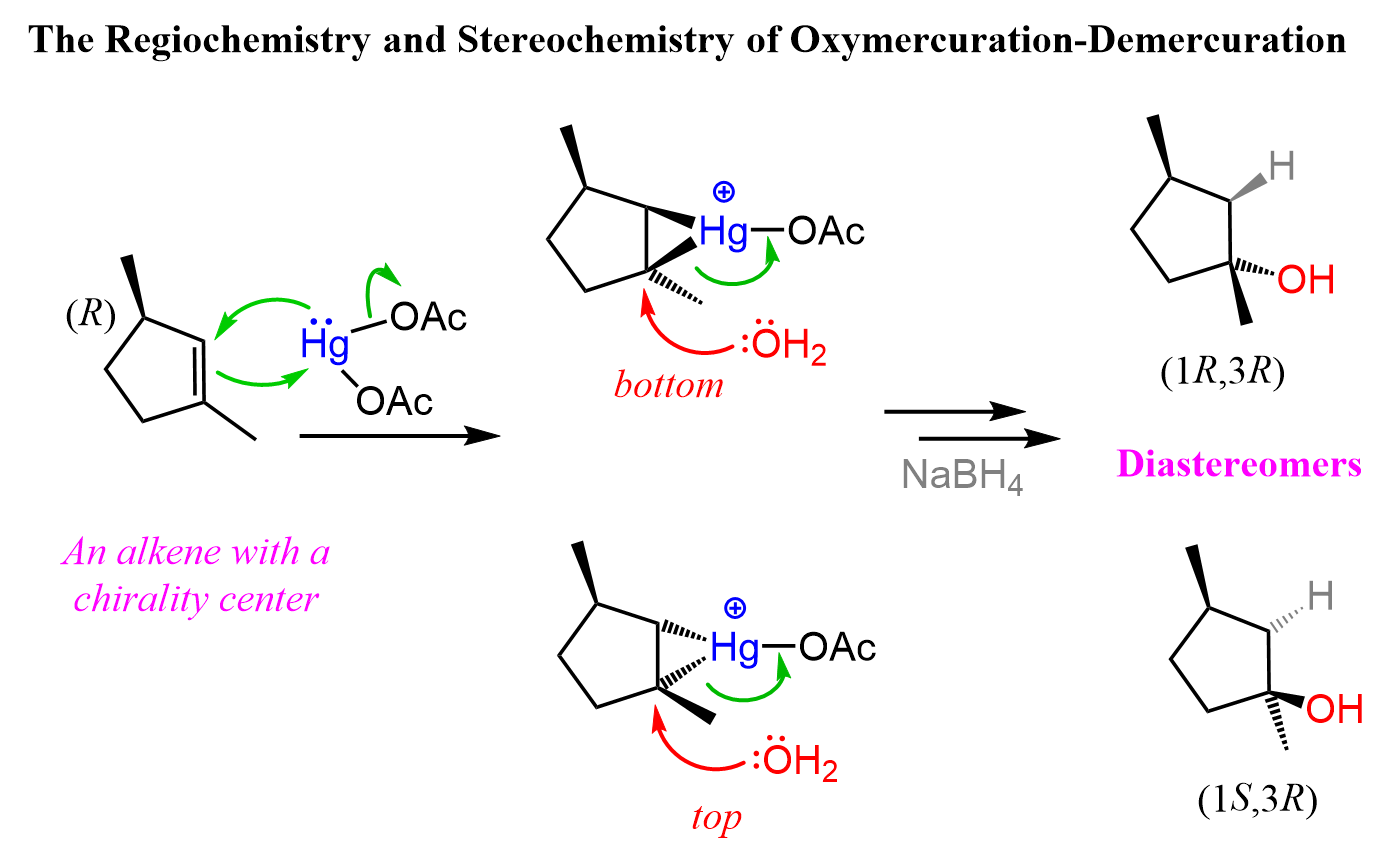
You can read more about the stereochemistry of the addition reactions to alkenes in this post.
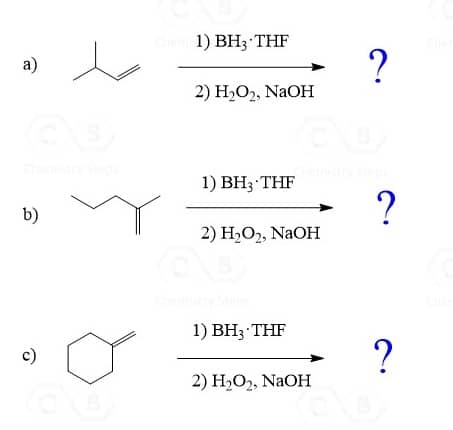
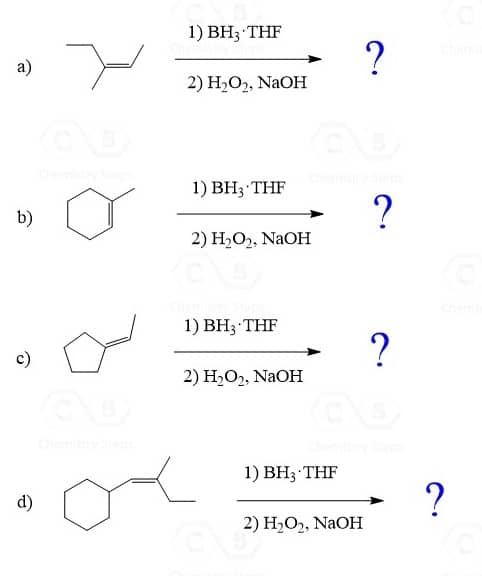
Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkenes
The hydroboration-oxidation does not go through a carbocation intermediate, and therefore, it adds the OH in anti Markovnikov fashion without any rearrangements:

Another difference between acid-catalyzed hydration and hydroboration is the stereochemistry of the addition. While hydroboration-oxidation is a syn addition, meaning both the hydrogen and OH add to the same face of the double bond, there is no stereoselectivity in the acid-catalyzed hydration as the carbocation is attacked from both sides of its planar geometry.

Check the corresponding articles for more details about these reactions.
In the end, let’s put together a scheme summarizing the regiochemical outcome of the three methods for the hydration of alkenes: