This is a 40-question, multiple-choice quiz to help you transition from General to Organic Chemistry. The topics covered in the quiz are listed below.
The quiz comes with a 1-hour video showing a detailed step-by-step solution to all the questions.
Stating Organic Chemistry this semester?
Check your knowledge base by taking this 40-question quiz covering the key concept you need to know when switching from General Chemistry to Organic Chemistry.
Electron Configurations
- This is the fundamental part to understand before starting the bonding and hybridization theories. You need to know about the energy, the number, the shape, and other characteristics of atomic orbitals and how electrons are accommodated in them.
Lewis structures
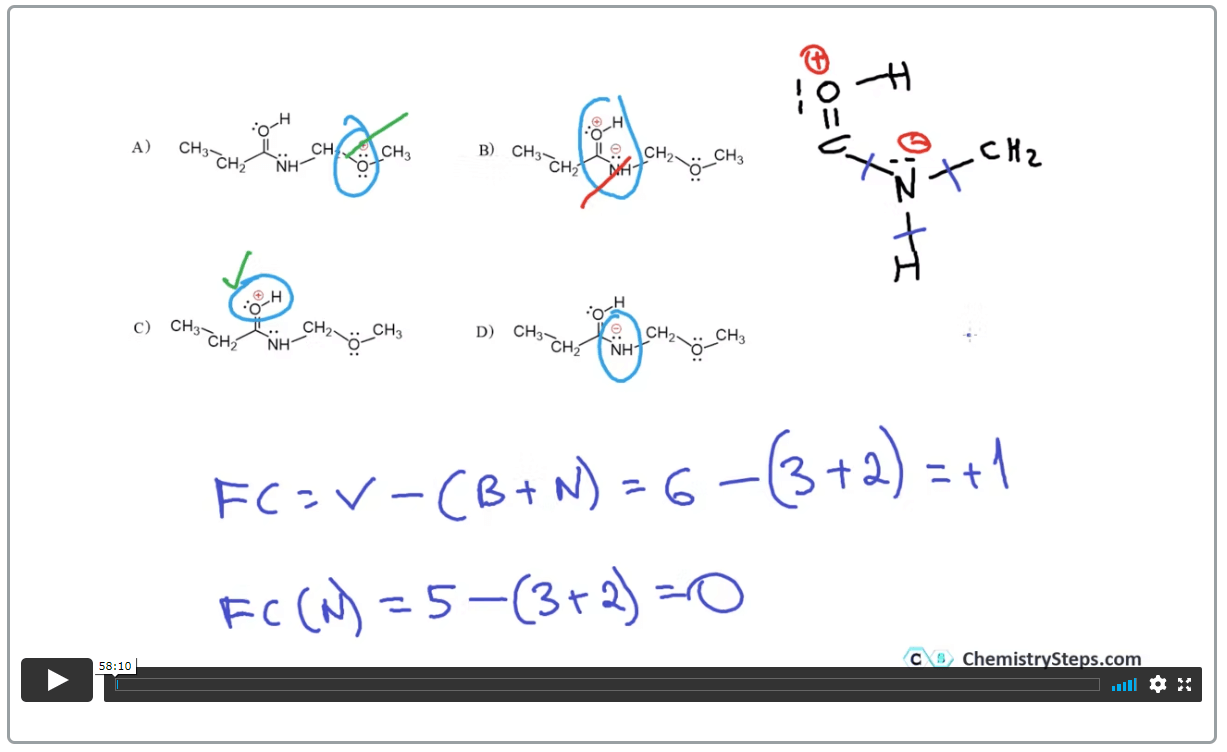
- The electron-dot model of representing valence electrons helps to understand the octet rule, bonding patterns of different elements, and predict the formal charges.
Select the correct Lewis structure for the following compound with a molecular formula C3H8:

Formal Charges
- The formal charge shows the imbalance of the electrons that the atom “owns” and shares when making a chemical bond. You can use a formula to calculate it, or the better alternative is practicing it till recognizing the bonding and number of lone pairs for the main elements in organic chemistry becomes natural. Here is an example question:
Select a structure(s) that contains an atom with an incomplete octet:

VSEPR Theory (Electron Molecular Geometries)
- Valence Shell Electron Repulsion Theory: Such a sophisticated name for the theory to help us predict the geometry of a molecule. It is very difficult once you devote some time to studying. However, it gets tricky here and there as we start talking about electron and molecular geometries and all the combinations of names and bond angles they bring up. Take your time to study and practice a lot since the good part of organic chemistry 1 focuses on the geometry of organic molecules, and in general, organic chemistry is about visualizing molecules in 3D and consequently understanding their reactions based on electron and steric effects.
Here is an example question:
The angle between carbon 2 and the lone pair on the nitrogen is:

Hybridization Theory
- This is another fundamental theory that helps to understand molecular geometries and reactivities of organic functional groups as well. You will need to master this in order to succeed in organic chemistry.
Here is an example question:
Which combination of orbital overlap describes the formation of the C=O bond in the following compound?
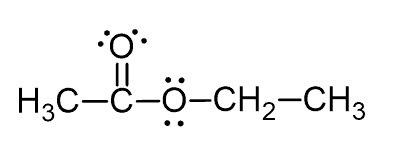
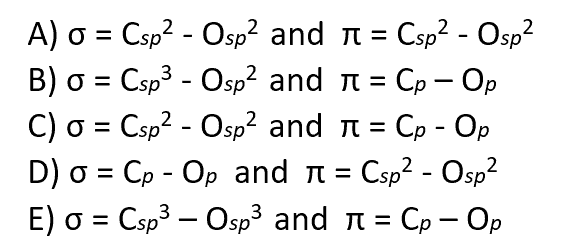
Most questions have a hint linked to the topic of the question. And if you feel like more feedback would be needed, you can head to the topic index and look for additional resources.