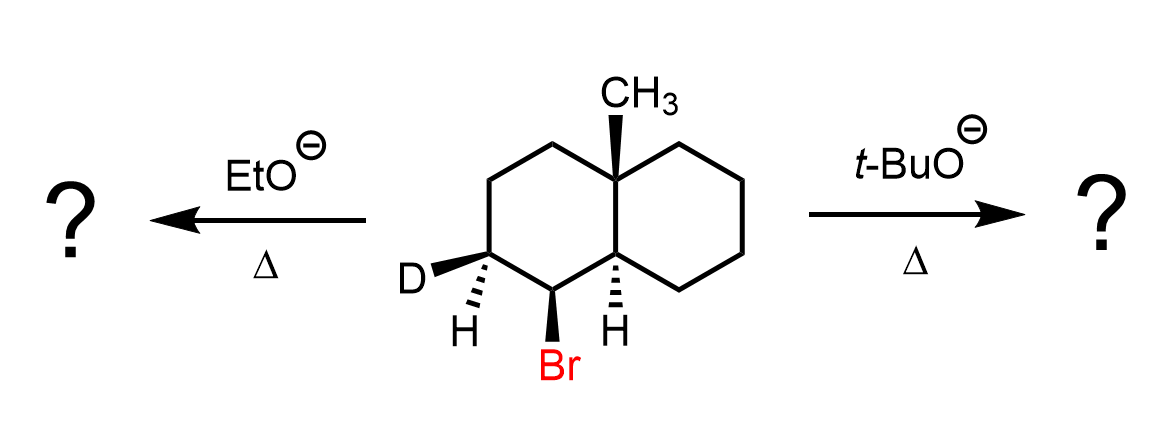
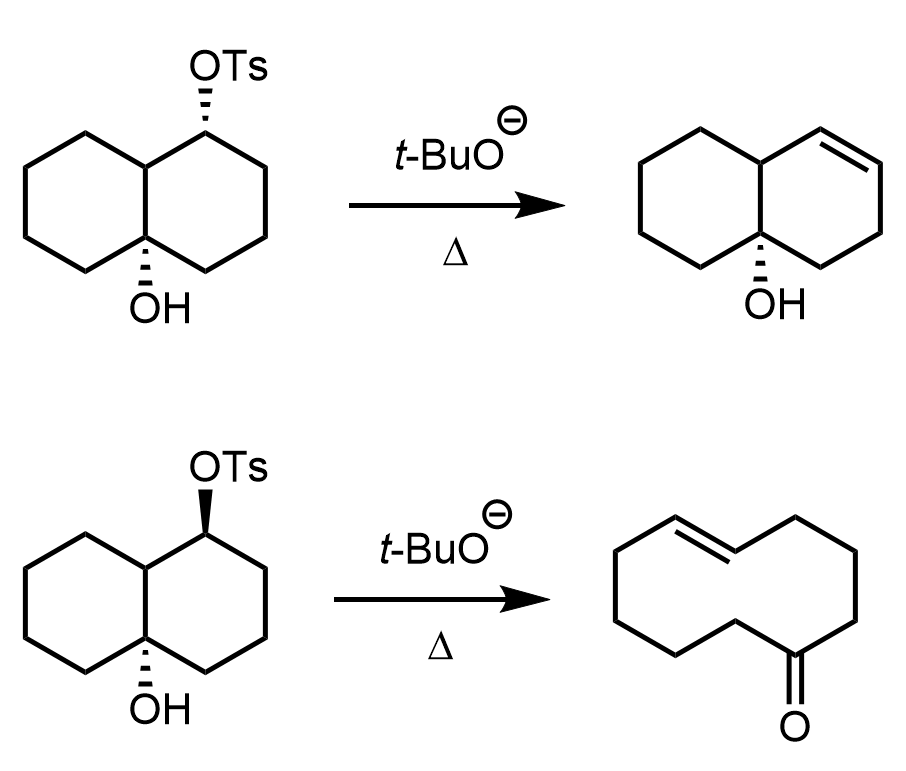
In this post, we will practice E2 elimination reactions, focusing on the mechanism and how to determine the major and minor products based on the structure of the substrate and the nature of the base. Common bases we will consider include sodium hydroxide, methoxide, ethoxide, tert-butoxide, DBU, and DBN.
We will also explore how factors such as stereoselectivity and stereospecificity influence the outcome of E2 reactions. Additionally, special attention will be given to the elimination reactions of cyclohexanes, where conformational analysis and the presence of antiperiplanar relationships play a critical role.