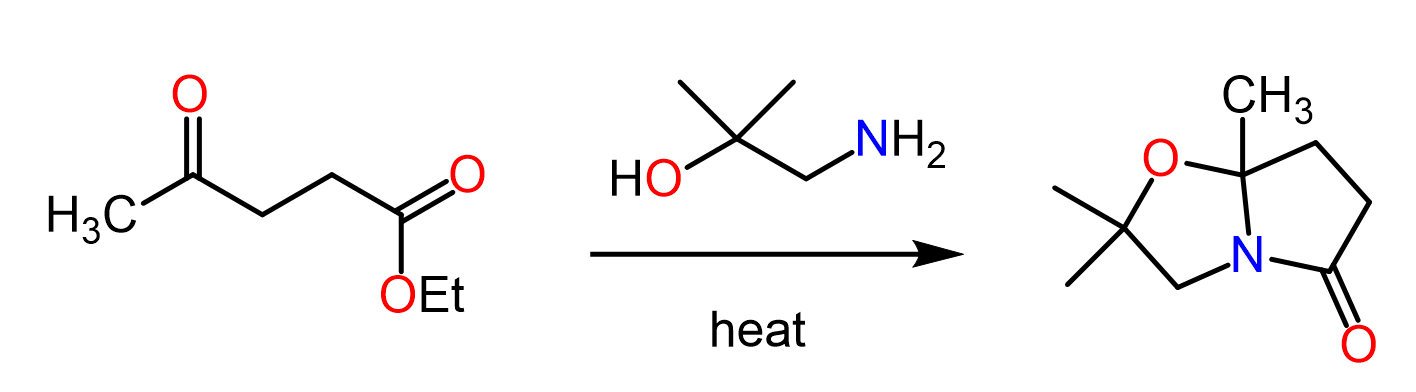
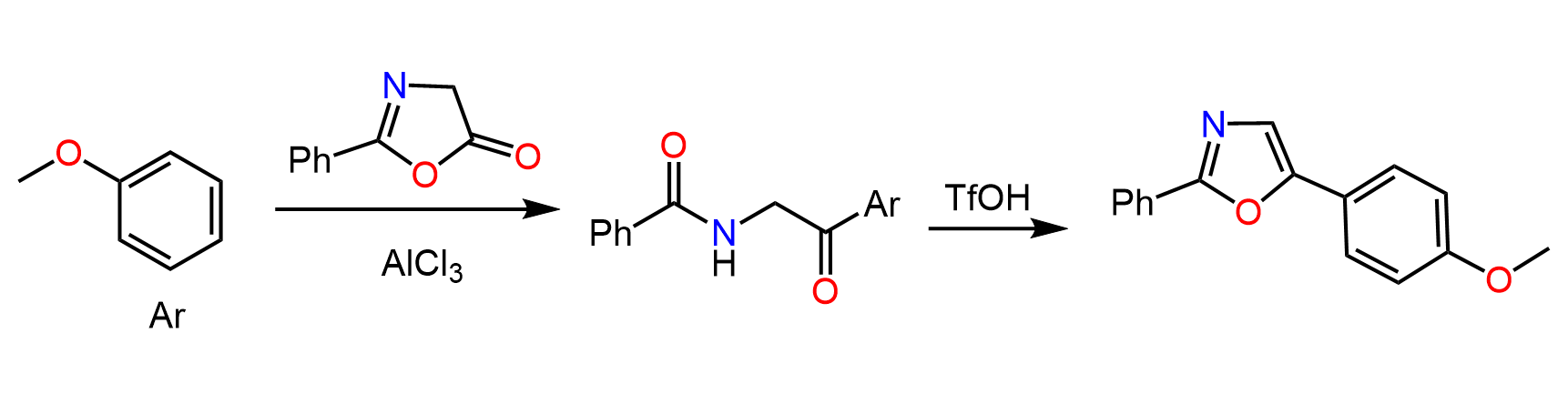
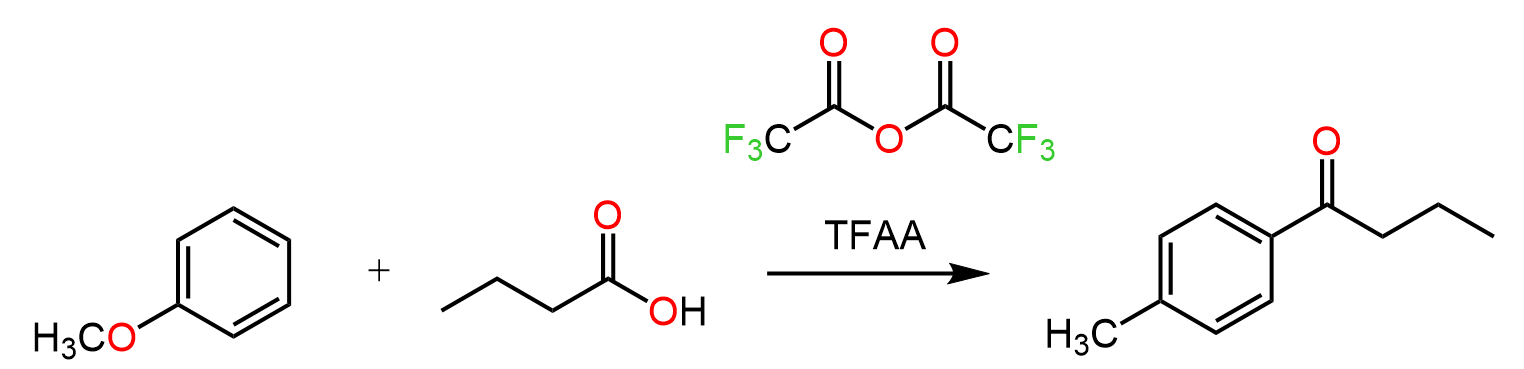
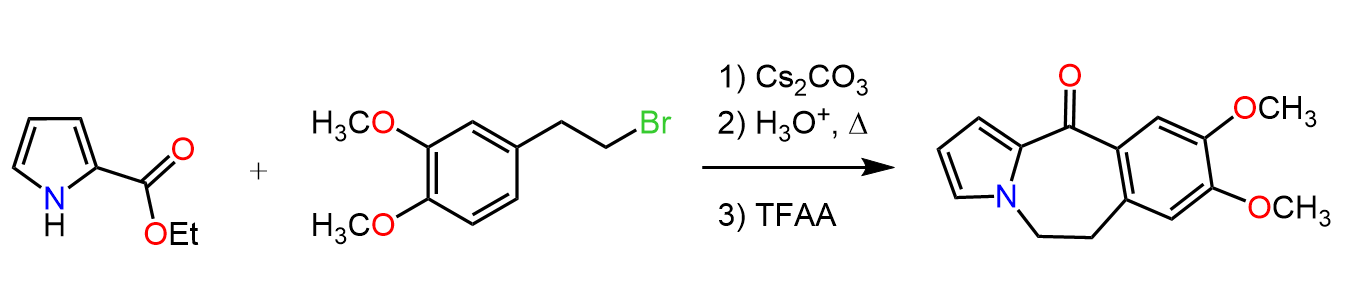
This article summarizes the main reactions of esters with associated practice problems. We covered the mechanism and other details about each reaction so, if you need to go over them, click on the corresponding links.
Let’s start with the hydrolysis of esters.
Esters can be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acid by acid base catalysis. The base-catalyzed hydrolysis, also called saponification, has the advantage of being irreversible.

Esters can be converted into primary, secondary and tertiary amides by an aminolysis reaction with ammonia, primary amine and a secondary amine respectively:

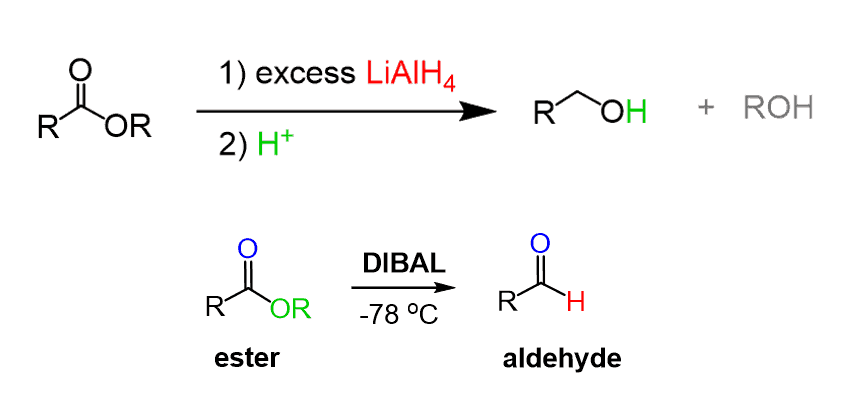
Esters can be reduced to alcohols or aldehydes using LiAlH4 and DIBAL respectively:
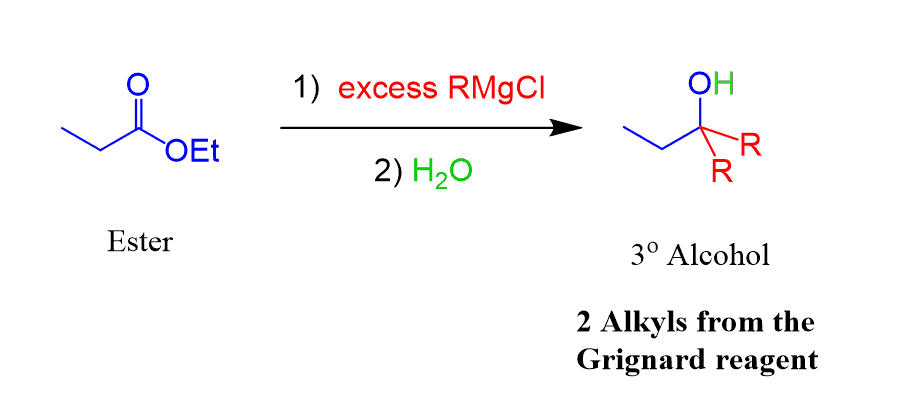
Reacting esters with excess Grignard reagent produces tertiary alcohols:
Below is the summary of ester reactions that you can use to work on the practice problems: