
General Features of Elimination
Practice
Label the ɑ and β carbons in each alkyl halide:
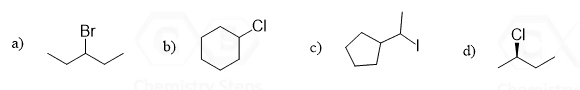
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Locate the β hydrogens and draw all possible elimination (regioisomers with different location of the double bond) products formed when each alkyl halide is treated with sodium ethoxide (CH3CH2O–Na+):
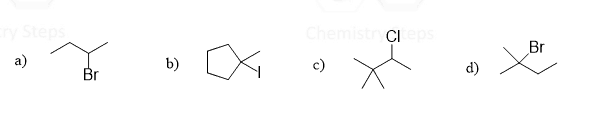
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Using curved arrows, draw the mechanism for the following elimination reactions, assuming a concerted process is taking place: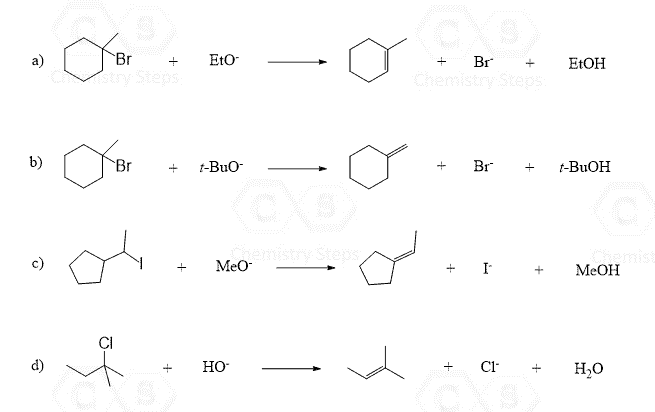
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
- The E2 Mechanism
- Zaitsev’s Rule – Regioselectivity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- The Hofmann Elimination of Amines and Alkyl Fluorides
- Stereoselectivity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- Stereospecificity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- SN2 and E2 Rates of Cyclohexanes
- Elimination Reactions of Cyclohexanes with Practice Problems
- POCl3 for Dehydration of Alcohols
- The E1 Mechanism with Practice Problems
- Regioselectivity of E1 Reactions
- Stereoselectivity of E1 Reactions
- How to tell if it is E2 or E1 Mechanism
- SN1 vs E1 Reactions
- Dehydration of Alcohols by E1 and E2 Elimination
- Mesylates and Tosylates as Good Leaving Groups
- Mitsunobu Reaction
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 – How to Choose the Mechanism
- Polar Protic and Polar Aprotic Solvents
- SN1 SN2 E1 or E2 – the Largest Collection of Practice Problems
- The Hammond Postulate
- The E1cB Elimination Mechanism
- Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Practice Quiz
- Reactions Map of Alkyl Halides

thank you!!!!!!!!!