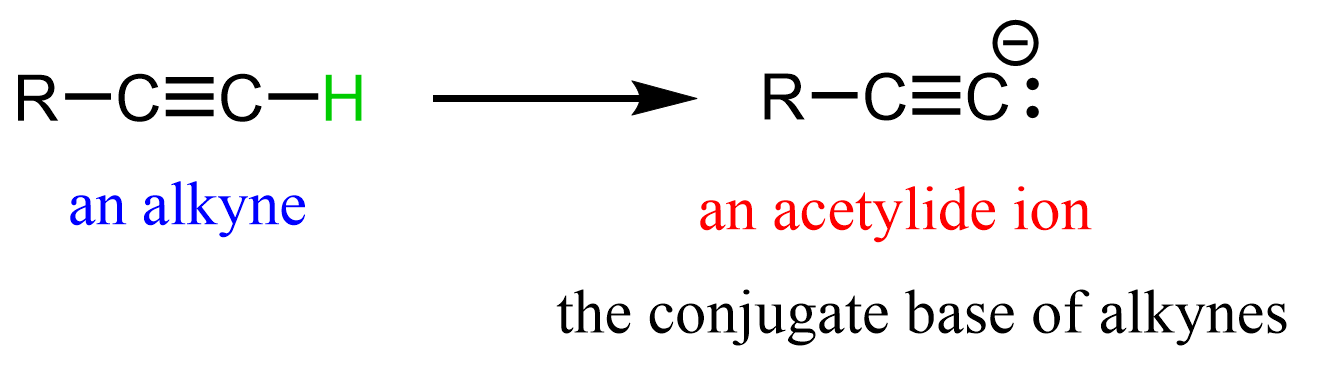
Acetylide ions are the conjugate bases of terminal alkynes:
What makes them different from the conjugate bases of alkanes and alkenes is that they are easier to prepare and use in other reactions. The reason for this is the higher acidity of the terminal alkyne proton, and we can use relatively weak bases to abstract them and prepare the acetylide ions. The pKa of alkynes is about 24, whereas the pKa of alkenes is ~44, and that of alkanes is ~50.

So, normally, the alkynes are deprotonated by sodium amide as the pKa of amines is ~38; therefore, their conjugate bases are strong enough to deprotonate the alkyne:
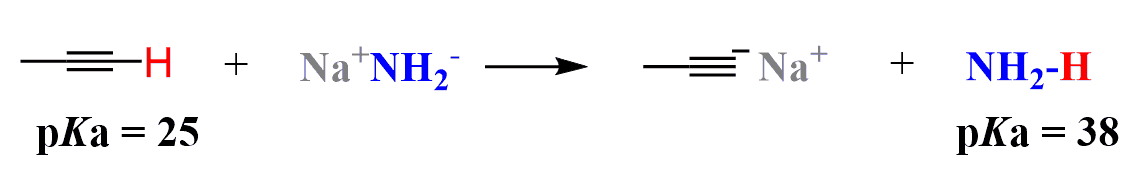
Remember that the stability of the conjugate base depends on several factors, and the first one is the atom that bears the negative charge. Generally speaking, electronegative atoms handle the negative charge better, which is why hydrocarbons are extremely weak acids; thus, their conjugate bases are very strong.
The Reactions of Acetylide Ions
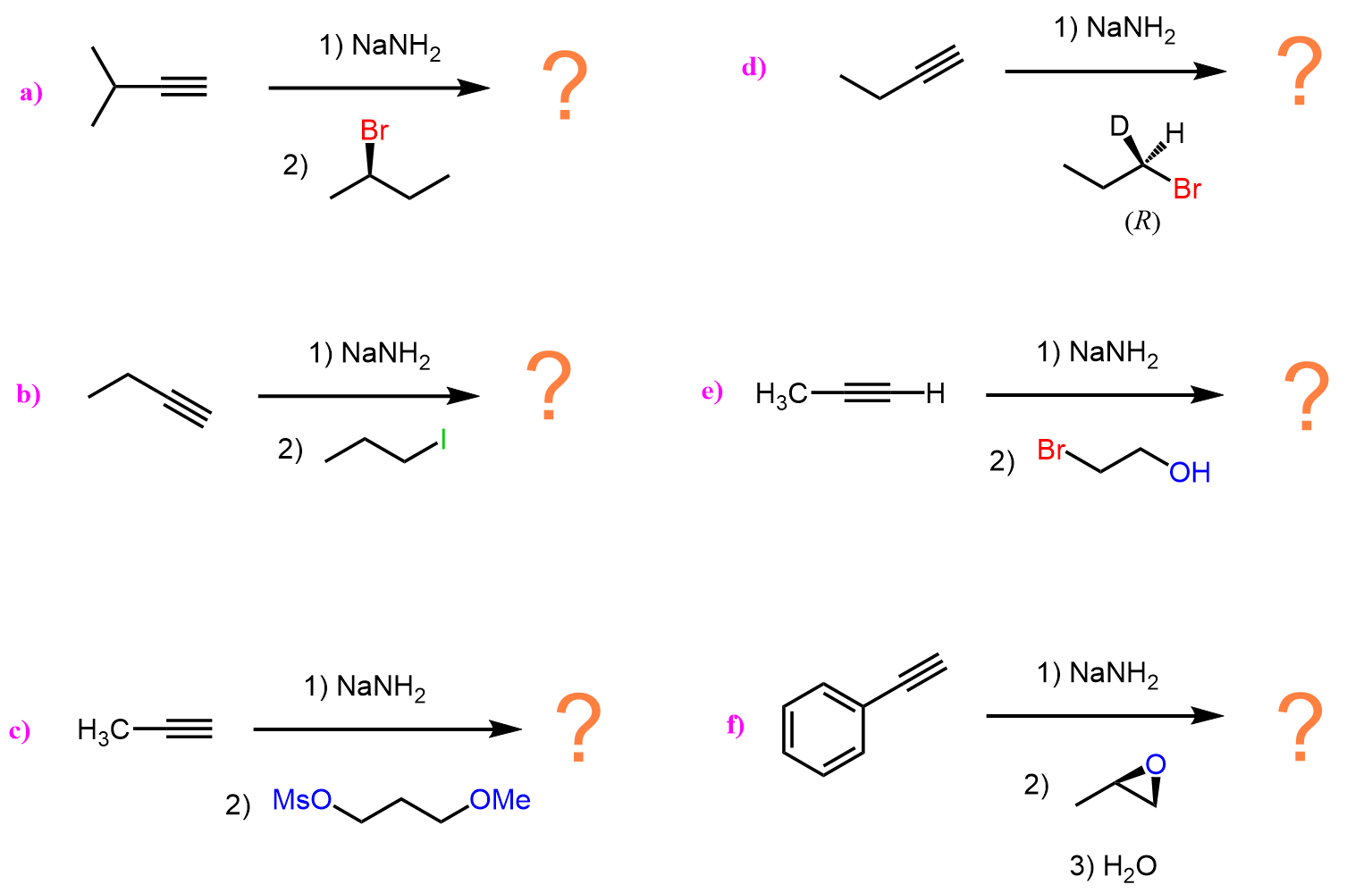
Although alkynes are relatively stronger acids than other hydrocarbons, the conjugate base acetylide ions are still strong bases and, what is important, very good nucleophiles. For example, they readily perform SN2 substitutions on methyl halides, primary alkyl halides, and epoxides:
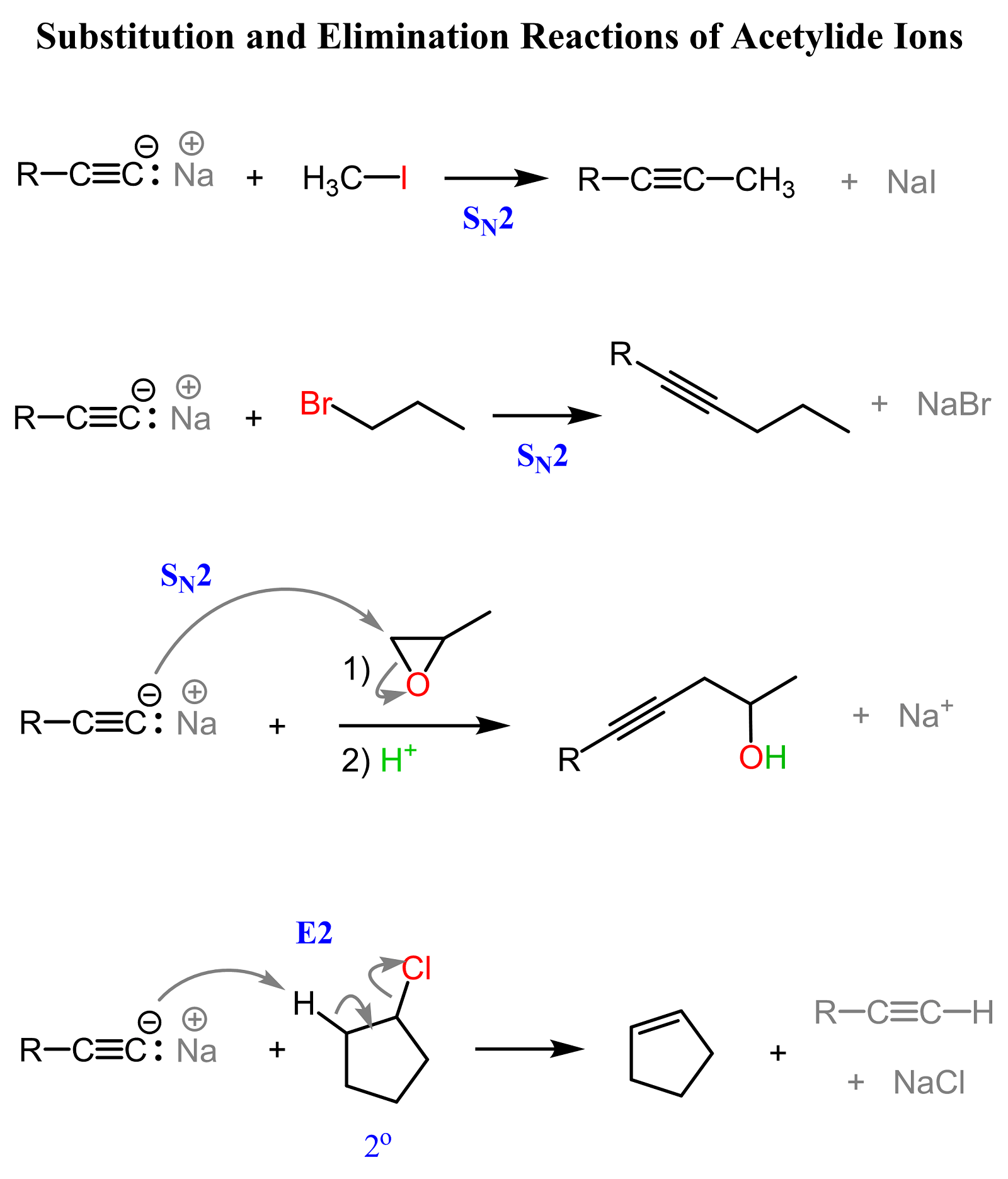
Notice that secondary alkyl halides are not the best option for these types of substitutions because the E2 pathway predominates when they are reacted with good nucleophiles that are also strong bases. You can read more about the comparison and competition of SN2 and E2 mechanisms here.
Acetylide Ions in Extending the Length of the Carbon Chain
If you haven’t yet talked about the Grignard reaction in class, this is likely the first reaction you see that allows you to extend the length of the carbon chain. Most of the SN2 reactions we have seen in the chapter on nucleophilic substitutions are simply replacing the leaving group with a halogen, SH, OH, and alkoxy (RO) groups, which means they do not make a new C-C bond. One such exception is the cyanide ion, which adds an extra carbon to the substrate:
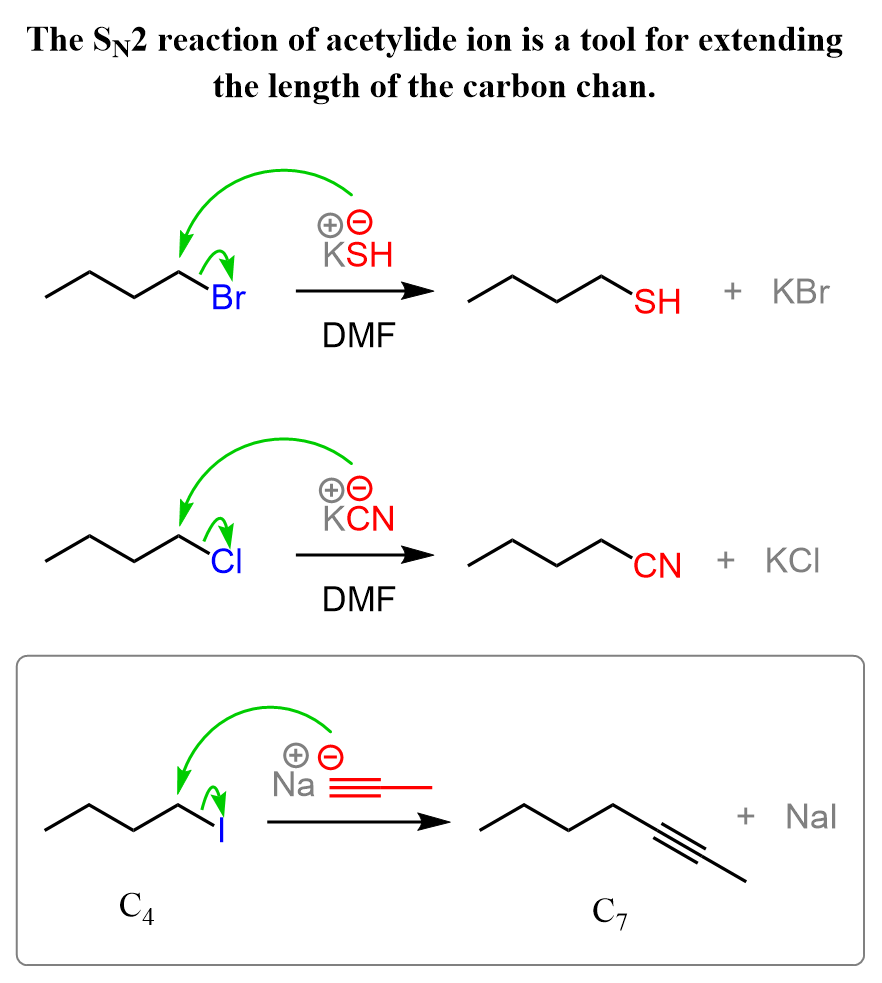
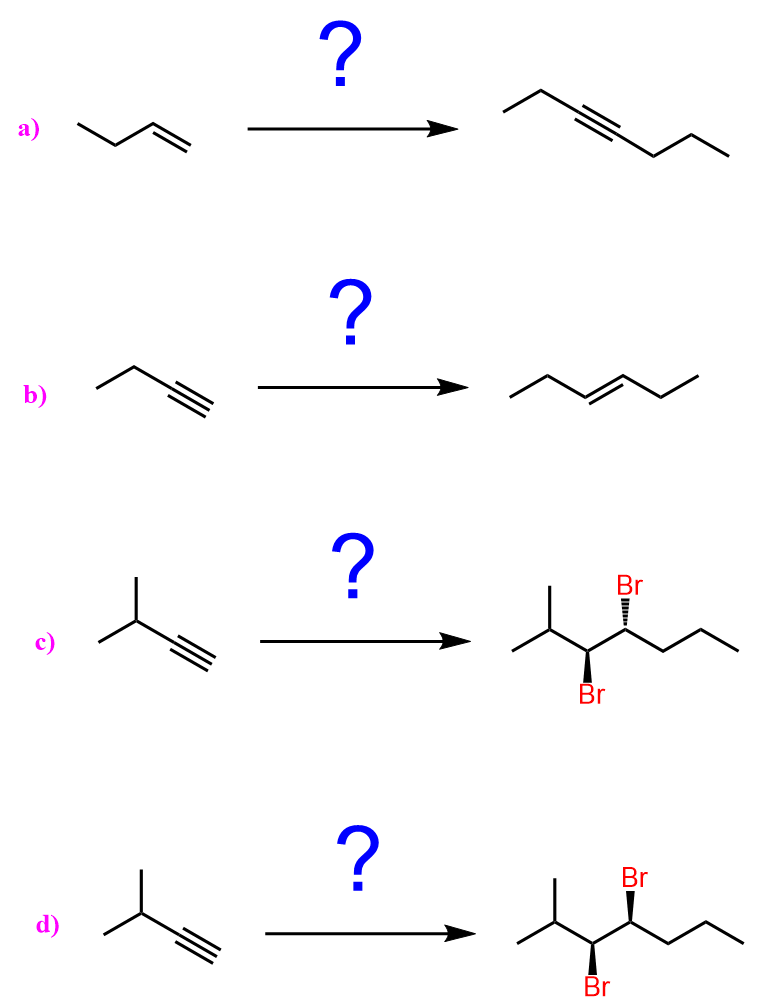
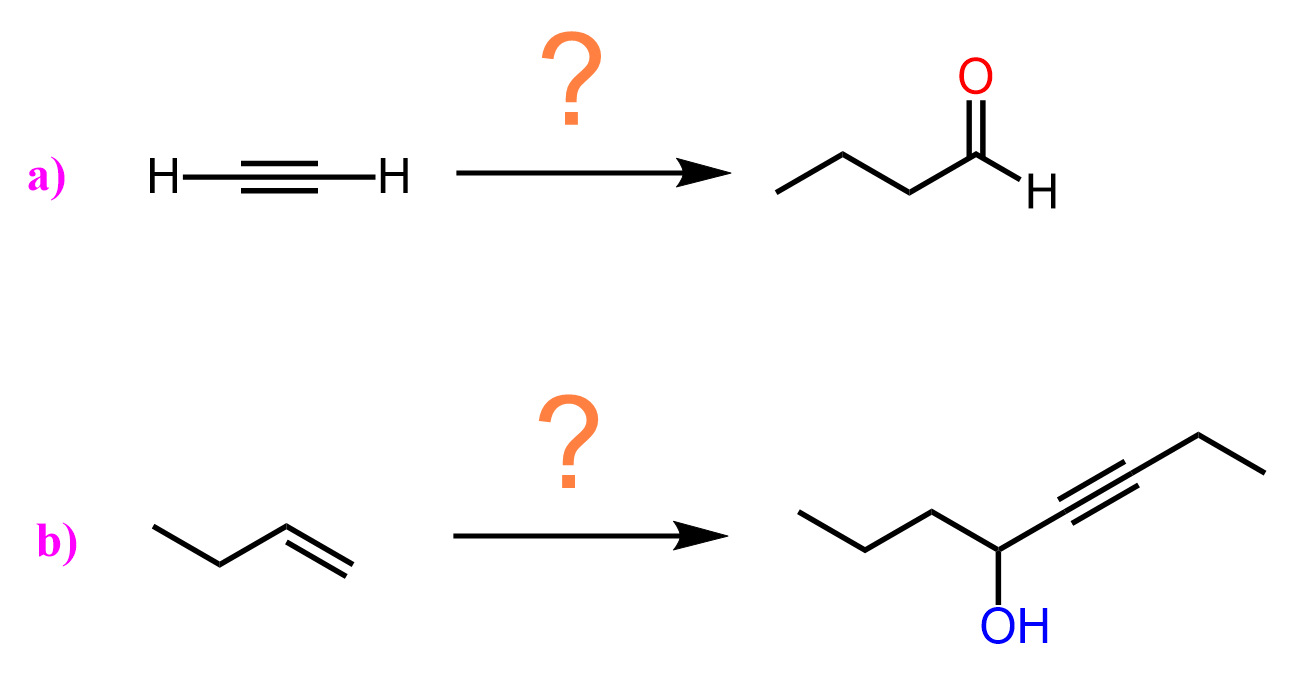
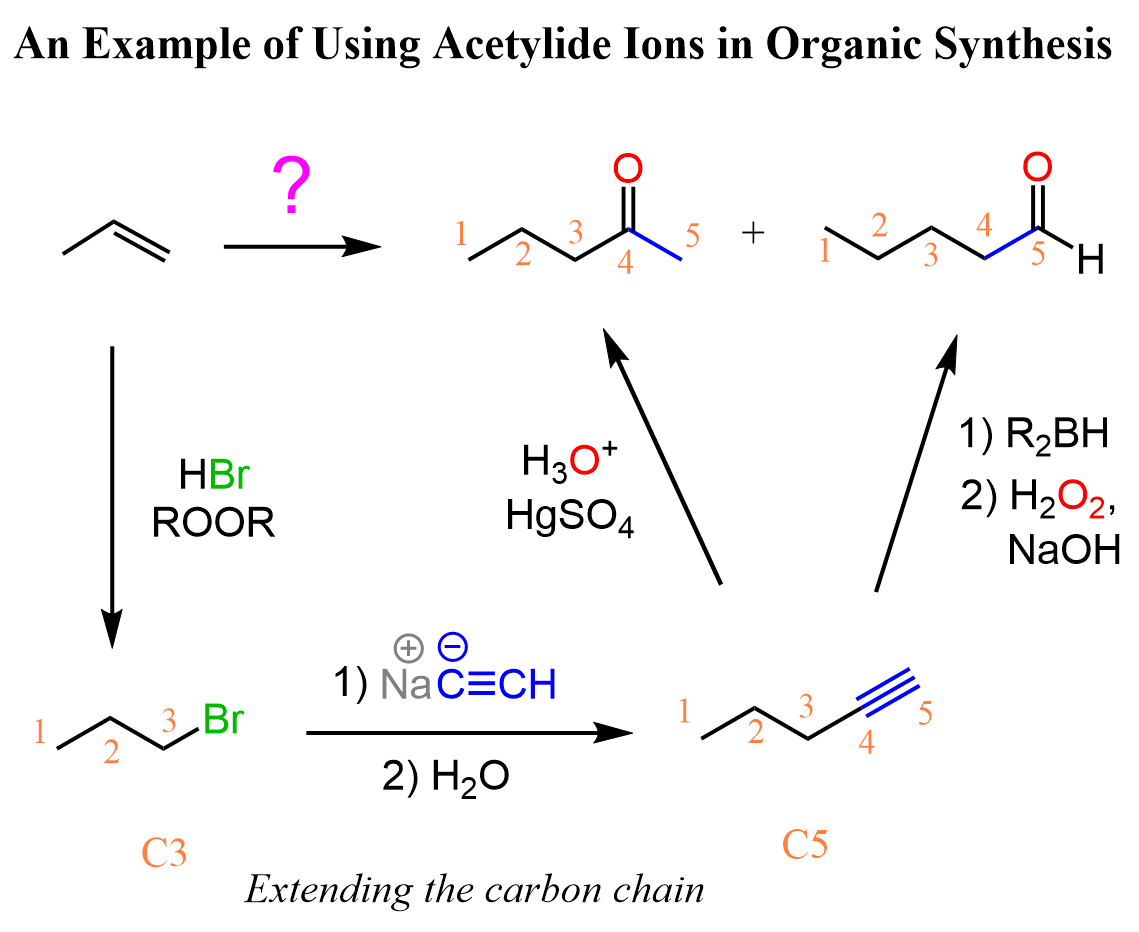
This feature of extending the length of the carbon chain is a great tool for synthesizing new molecules and achieving some functional group transformations. For example, let’s see how we can use the introduction of an acetylide ion to convert the following alkene to a ketone or aldehyde:
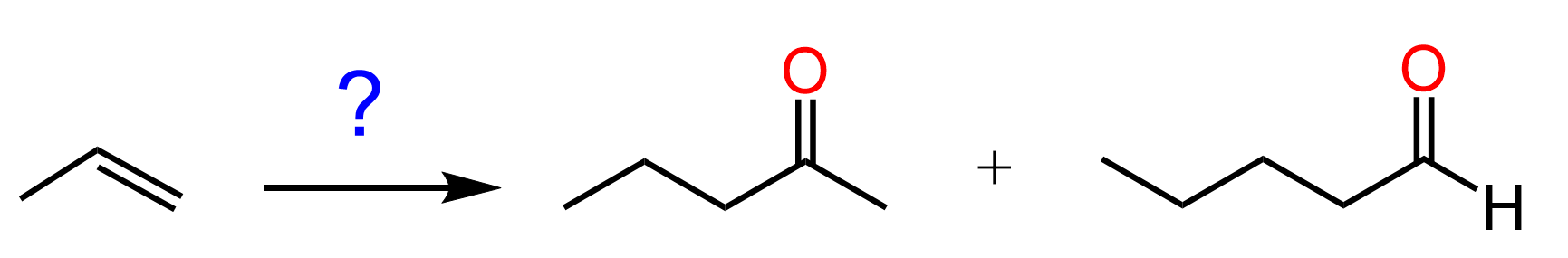
Notice that both products have longer carbon chains, which is most likely an indication that we need to use an acetylide ion. The alkene, on the other hand, cannot be reacted with an acetylide ion, so what we can do is convert it into an alkyl halide and then react with an acetylide ion. The substrate has three carbon atoms, whilst both products have five carbon atoms. Therefore, the acetylide ion must be the conjugate base of acetylene:
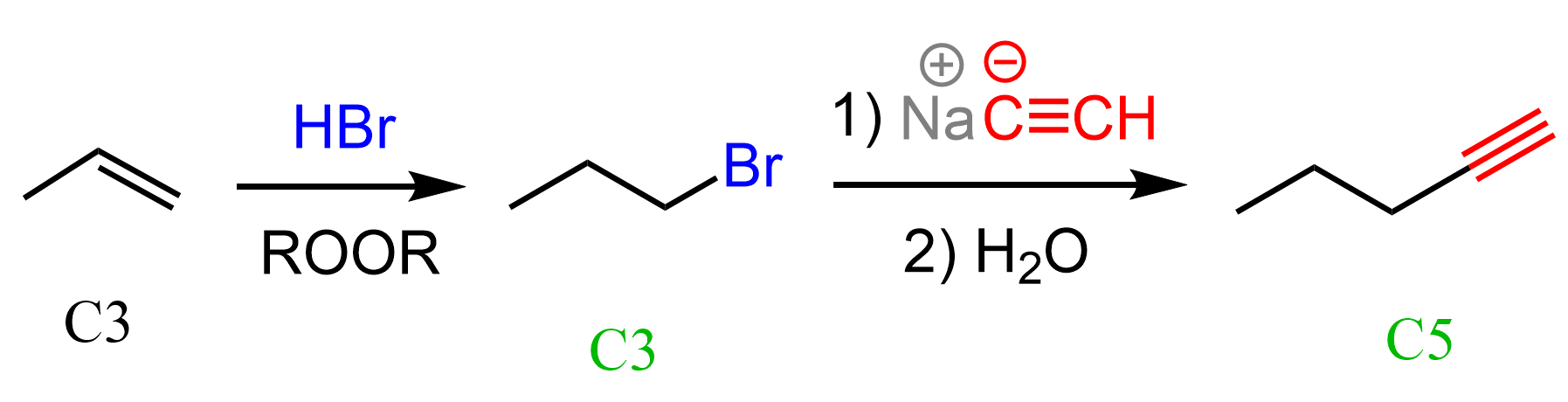
The water in the second may be optional, but it is there just to react with any excess of the acetylide ion. This is called an aqueous workup, and it is said to quench the reaction.
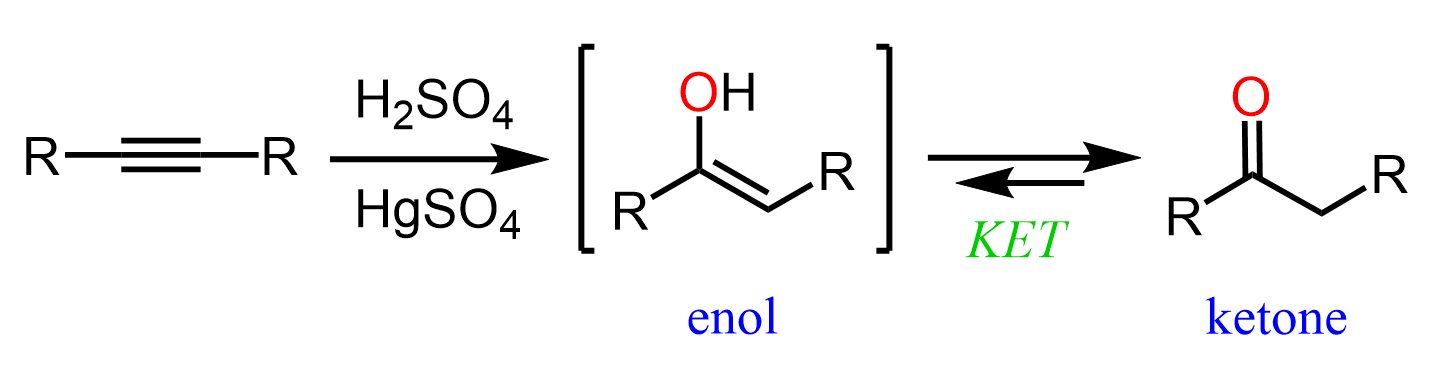
Once we have an intermediate alkyne with five carbon atoms, we can convert it to an aldehyde or a ketone by a Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov hydration of the triple bond. Remember, the Markovnikov hydration can be achieved by acid- or Hg2+– catalyzed hydration of the triple bond, and for anti-Markovnikov addition of water, we use the hydroboration-oxidation with alkyl boranes:
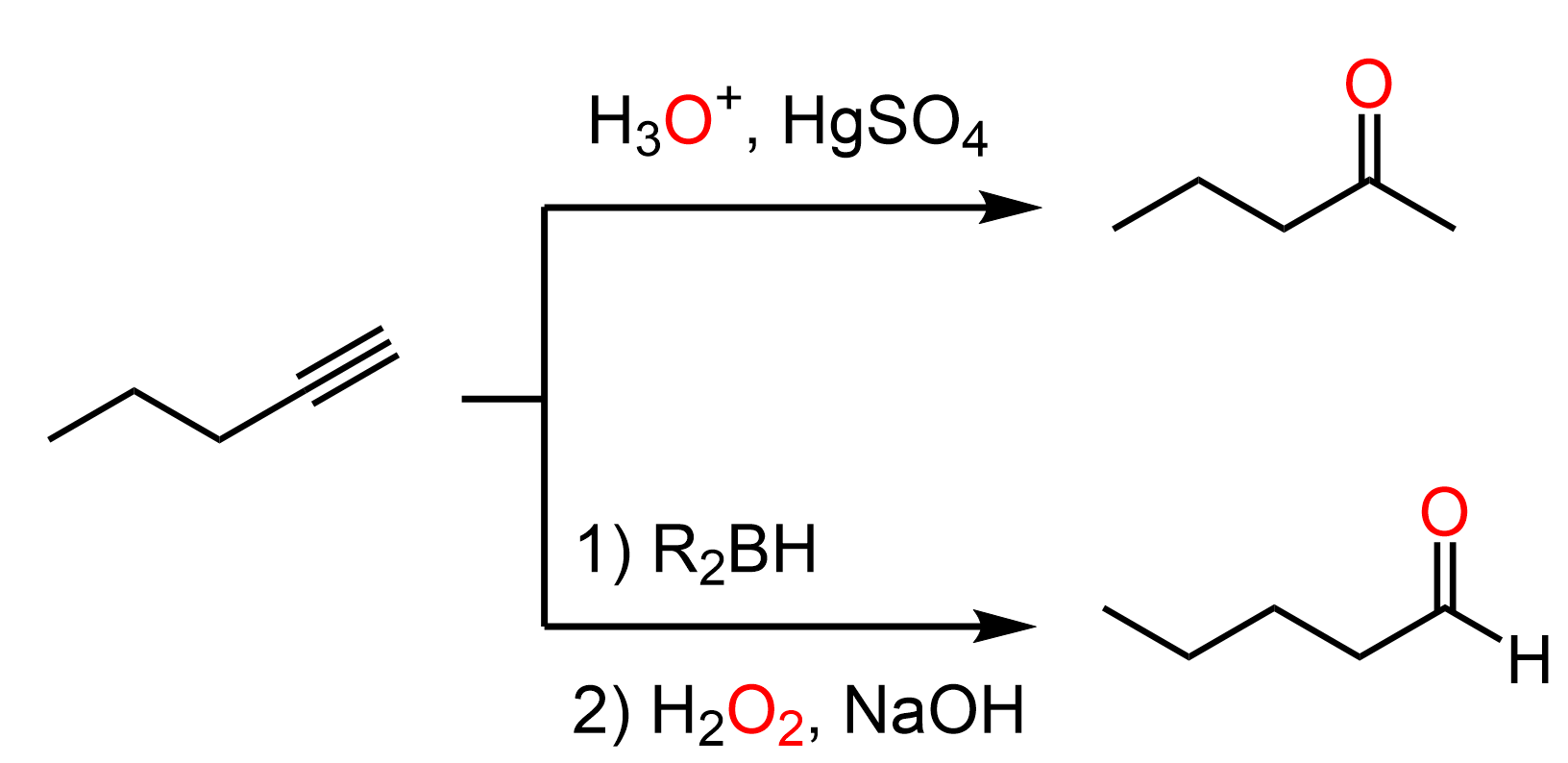
In both cases, an enol intermediate is formed, which undergoes a keto–enol tautomerization, giving the final carbonyl product.
Let’s summarize this transformation involving the use of the acetylide ion in one synthetic scheme.
Another strategy for extending the length of the carbon chain that you may have covered is the Grignard reaction, and this article is about the use of acetylide ions and Grignard reagents in organic synthesis, with some practice problems.