ChatGPT said:
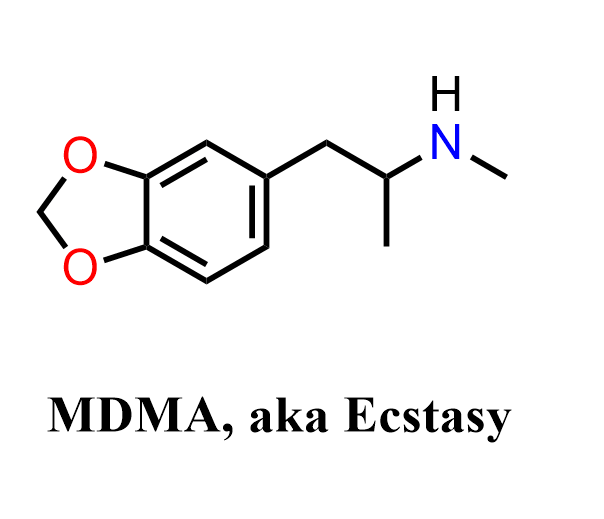 MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine), commonly known as Ecstasy, is a synthetic psychoactive compound that combines stimulant and empathogenic effects. It was first synthesized in the early 20th century and later investigated for potential therapeutic uses, particularly in psychotherapy, before becoming widely known as a recreational drug. MDMA affects neurotransmitter systems involving serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which explains its characteristic effects on mood, empathy, and sensory perception. Because of its non-medical use and associated health risks, MDMA is now a tightly regulated substance in most countries.
MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine), commonly known as Ecstasy, is a synthetic psychoactive compound that combines stimulant and empathogenic effects. It was first synthesized in the early 20th century and later investigated for potential therapeutic uses, particularly in psychotherapy, before becoming widely known as a recreational drug. MDMA affects neurotransmitter systems involving serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which explains its characteristic effects on mood, empathy, and sensory perception. Because of its non-medical use and associated health risks, MDMA is now a tightly regulated substance in most countries.
In this practice problem, we examine a conceptual synthetic pathway to MDMA starting from phenol, to review key ideas in electrophilic aromatic substitution and other functional group transformations.
As with all examples in this section, this discussion is presented solely for educational purposes and is not intended to represent a practical or real-world method of preparation.
Practice
Add the missing reagents and intermediates in the synthesis of MDMA.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
