Let’s compare the following two Diels-Alder reactions:
The first one is a reaction between a symmetrical diene and a dienophile and the second one is a reaction of an unsymmetrical diene and a dienophile.

What is interesting here is that the first reaction produces only one product (we will disregard the stereochemistry for now), while the second one can give a mixture of two regional (constitutional) isomers. These isomers are formed as a result of the two possible orientations (A and B) that the diene and dienophile can have. You can simply flip one of the reactants upside down to better visualize the formation of two isomers:
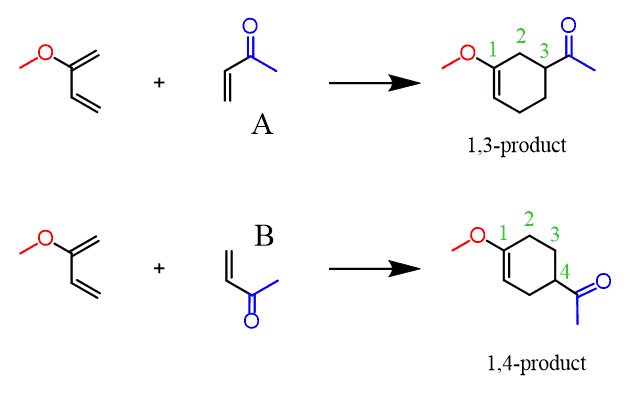
This is the regiochemistry or the regioselectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction. And the question is which of these regioisomers is the major product?
It turns out that the 1,4-product is the major regioisomer which means that the diene and dienophile follow alignment B in the transition state of the reaction:
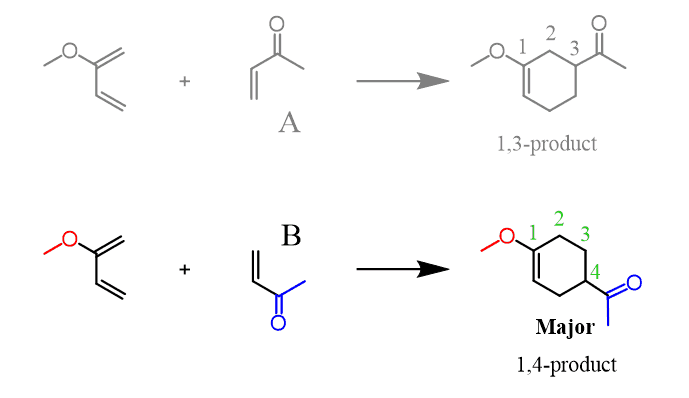
How do I figure this out for any Diels-Alder reaction?
This regioselectivity is a result of the electron distribution in the diene and the dienophile. The most electron-rich carbon of the diene reacts with the mot electron-deficient carbon of the dienophile.
You have two ways to determine the proper alignment of the diene and the dienophile.
The first one is to draw the resonance structures of the diene and dienophile placing the formal charges on the terminal atoms and align the molecules next to each other pairing the opposite charges:

Remember that the Diels-Alder reaction follows a concerted mechanism and there is no (ionic) intermediates involved. We are only doing this to predict the major product by connecting the most electron-rich carbon of the diene to the most electron-deficient carbon of the dienophile.
Is there a shorter route?
You can also predict the major regioisomer of a Diels-Alde reaction without drawing the resonance forms. Simply place the molecules next to each other and draw the curved arrows connecting the first two carbons of the diene and the dienophile;
The correct alignment is the one that supports the electron flow from the electron-donating diene substituent to the electron-withdrawing group of the dienophile (electron-flow method):
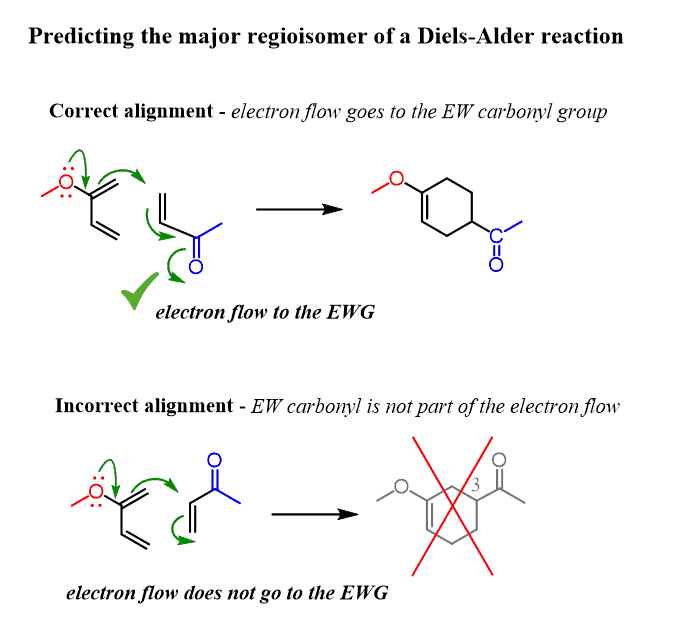
Notice again that this is not the mechanism of the Diels-Alder reaction! It is only to quickly predict the major regioisomer of the product. Once you have determined the correct alignment, you can now draw the actual mechanism.
What if the CH3O- is on the other carbon?
Let’s also look at an example where the electron-donating group of the diene is on carbon number 1 (1-substituted diene):
This time, we can first try the electron-flow method:
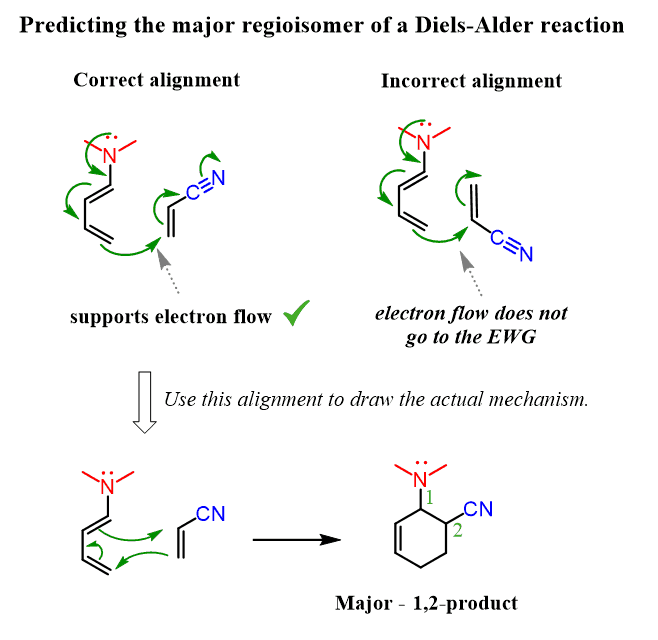
Making a short summary, we can see that depending on the structure of the diene, the 1,2 or 1,4-product is obtained. The 1,3-product is never favored.
Stereochemistry of the unsymmetrical Diels-Alder reaction
In reactions of both 1-substituted diene and 2-substituted diene, there is a formation of a stereogenic center(s) which we ignored so far to avoid additional complications. And depending on what your instructor asks, you may not need this at all. However, we will address this as well.
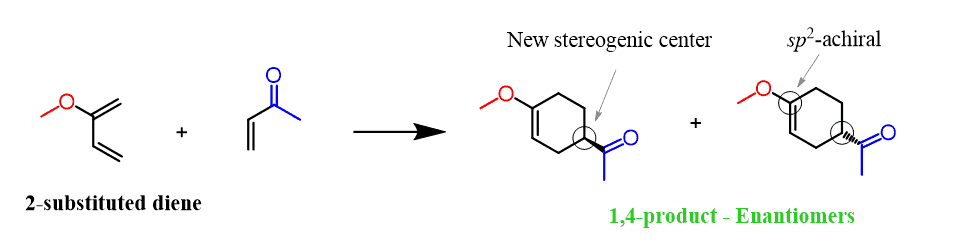
Let’s start with the 2-substituted diene since this one is a bit easier. And the reason is that the product here has only one stereogenic center, therefore, it is a racemic mixture of enantiomers:
The reaction of a 1-substituted diene forms a product (major regioisomer) with two stereogenic centers and this means that in total, four stereoisomers are possible. These are a mixture of enantiomers and diastereomers and if that concept still gives you a headache, you can check this article one more time.
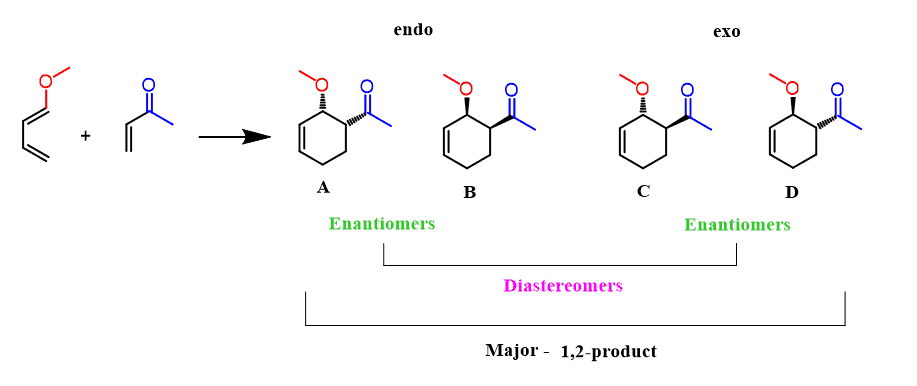
There is also the endo and exo stereochemistry to consider here and it may look overwhelming, but let’s try to figure this out.
We need to bring back the endo-rule for the reactions of cyclic dienes for a moment. For example, suppose you needed to predict the major product of this Diels-Alder reaction:
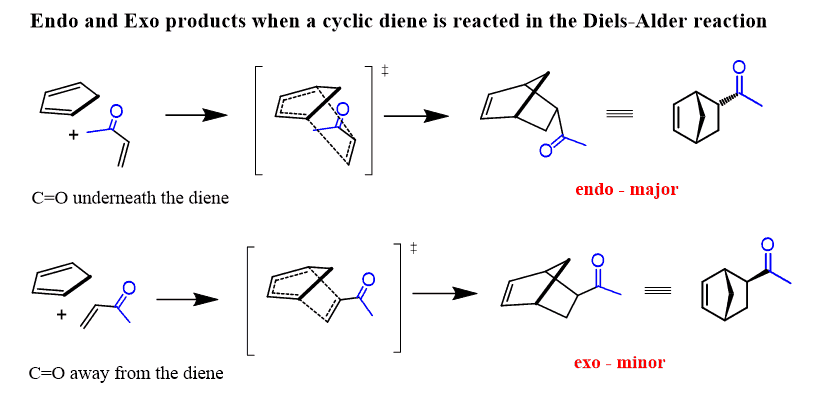
Remember, the endo product is formed when the electron-withdrawing group of the dienophile is pointing towards the π electrons of the diene. This decreases the energy of the transition state because of a favorable interaction between the non-bonding orbitals of the diene and the electrons of the dienophile.
Now, following the same pattern, let’s draw this mechanism for the unsymmetrical acyclic diene with an imaginary carbon that we add to temporarily turn it into a cyclic diene:
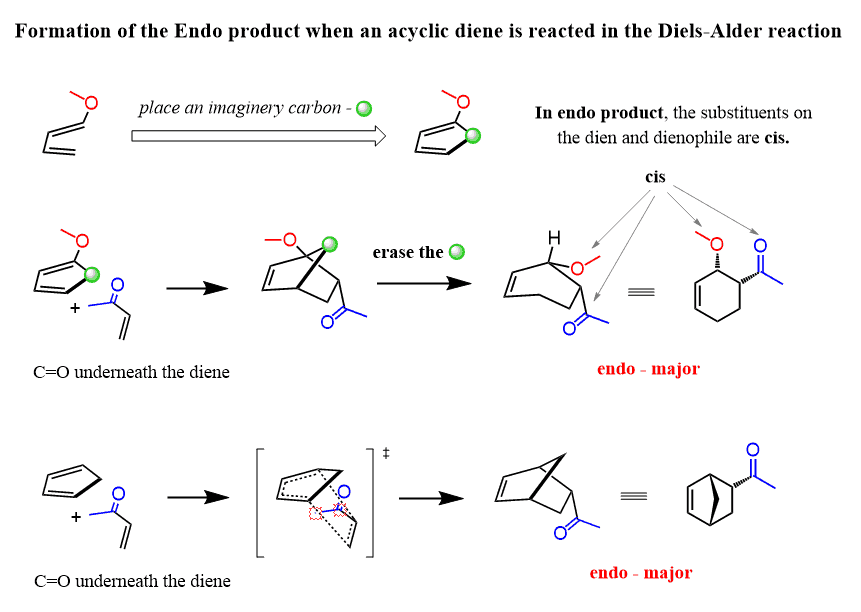
Notice that in the endo product, the substituents on the diene and dienophile are cis as they are both pointing to the same direction. And this is the general definition of the endo product pertaining to cyclic and acyclic dienes:
The exo product is formed when the electron-withdrawing group of the dienophilie is pointing away from the π electrons of the diene:
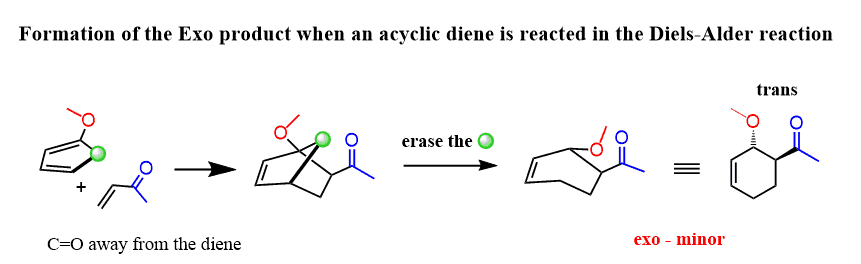
Notice that in the exo product, the two groups of the diene and the dienophile are in trans geometry.
Each endo and exo products are formed in the form of two enantiomers and each endo-exo product is a pair of diastereomers:
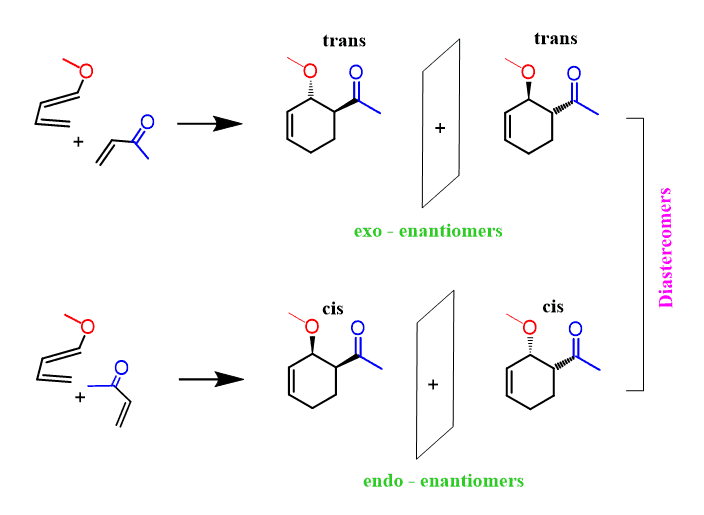
Let’ recap. If you are asked to determine the regiochemistry only, then follow the electron-flow method or the draw the resonance structures and align the formal charges accordingly.
If, in addition to the regiochemistry, you also need to address the stereochemistry of the reaction, place an imaginary carbon to temporarily convert the diene into a cyclic molecule, and follow the rules that you learned in the endo and exo products of the Diels-Alder reaction.
Remember, endo is the kinetic product of the reaction and most often is considered as the major product. However, at higher temperatures, the thermodynamic exo product may dominate since it is the more stable stereoisomer.