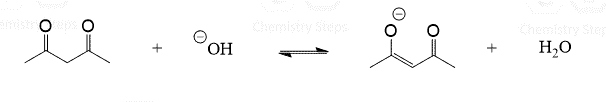
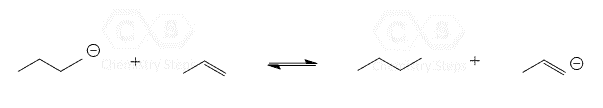
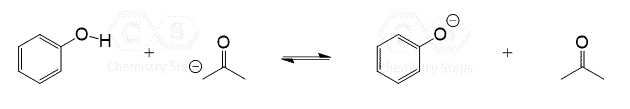
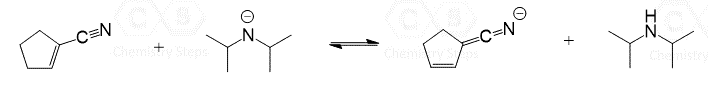
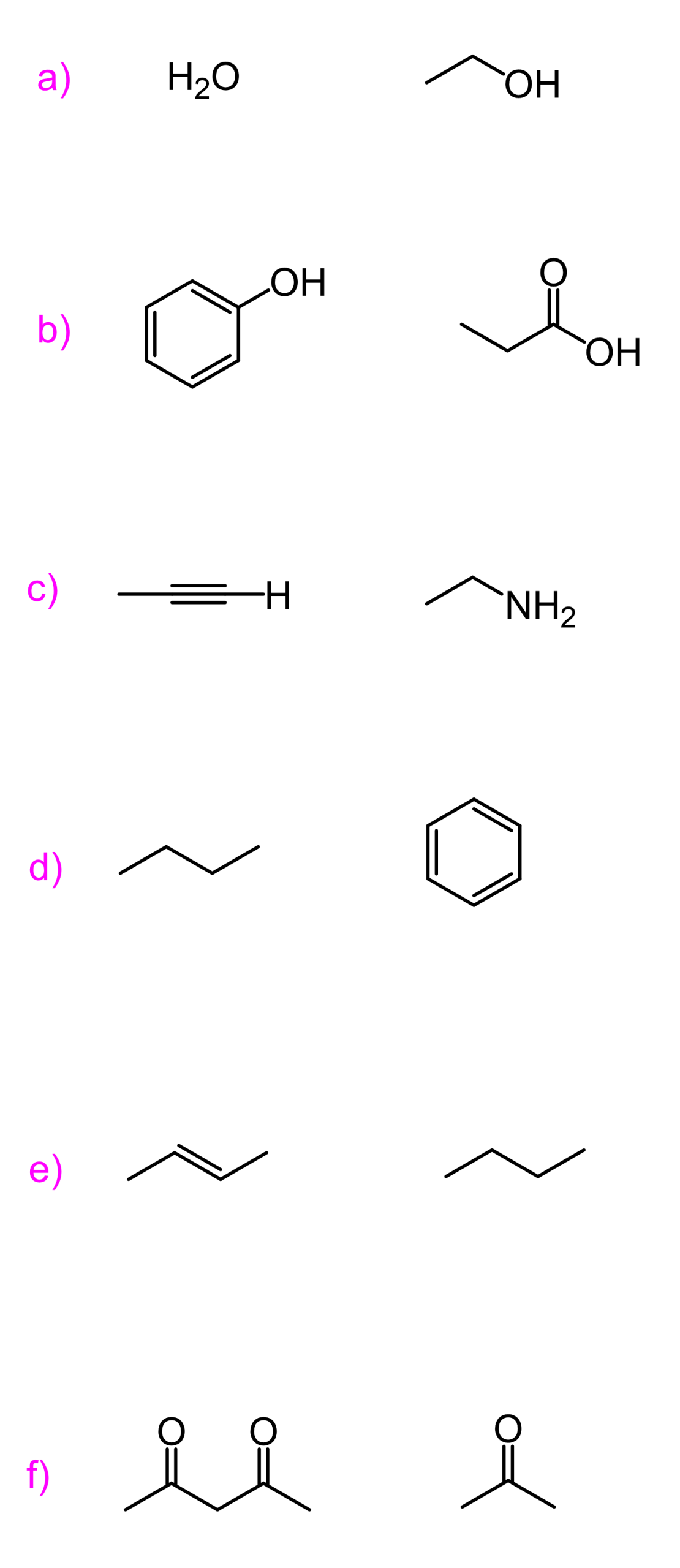
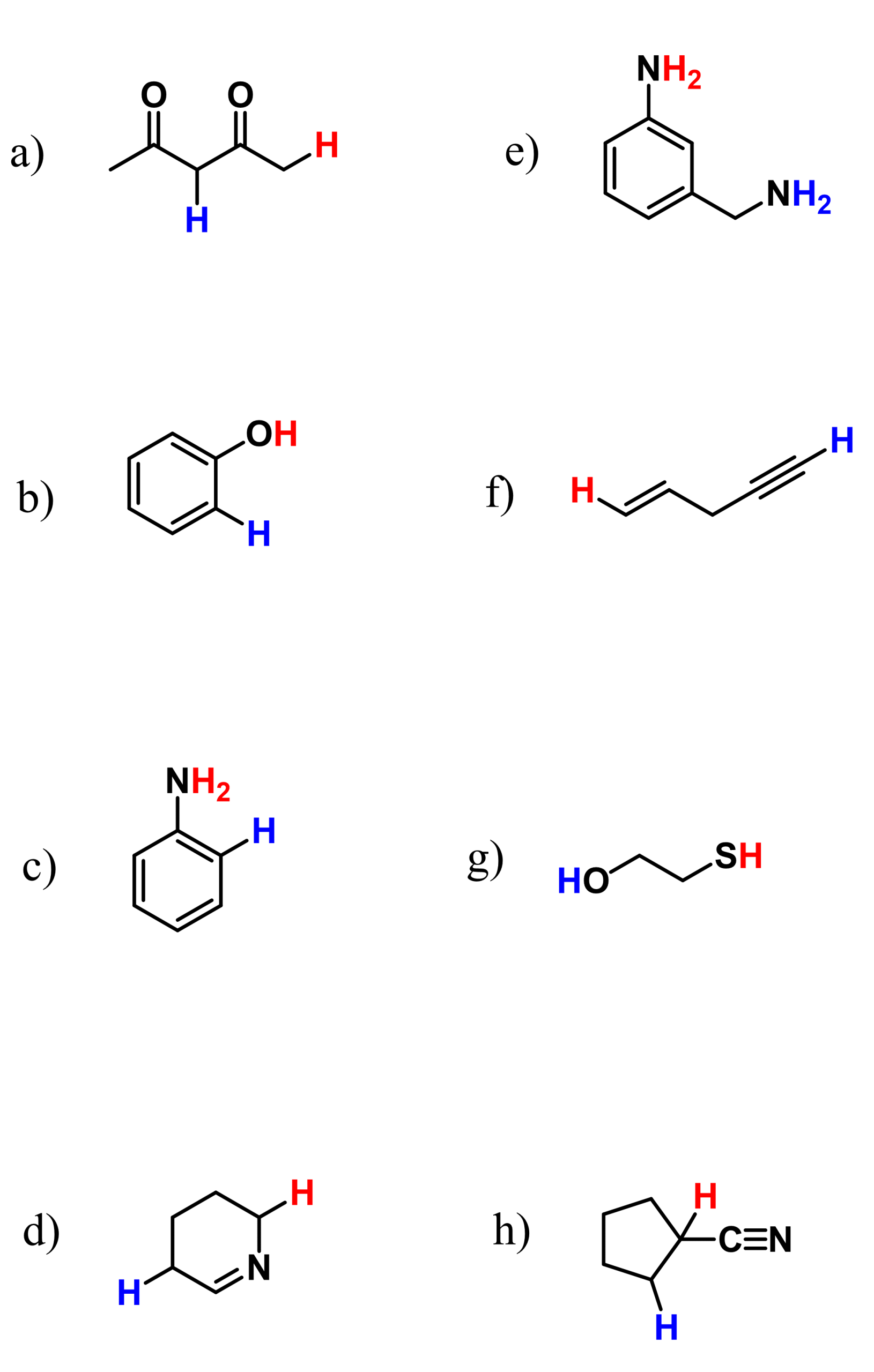
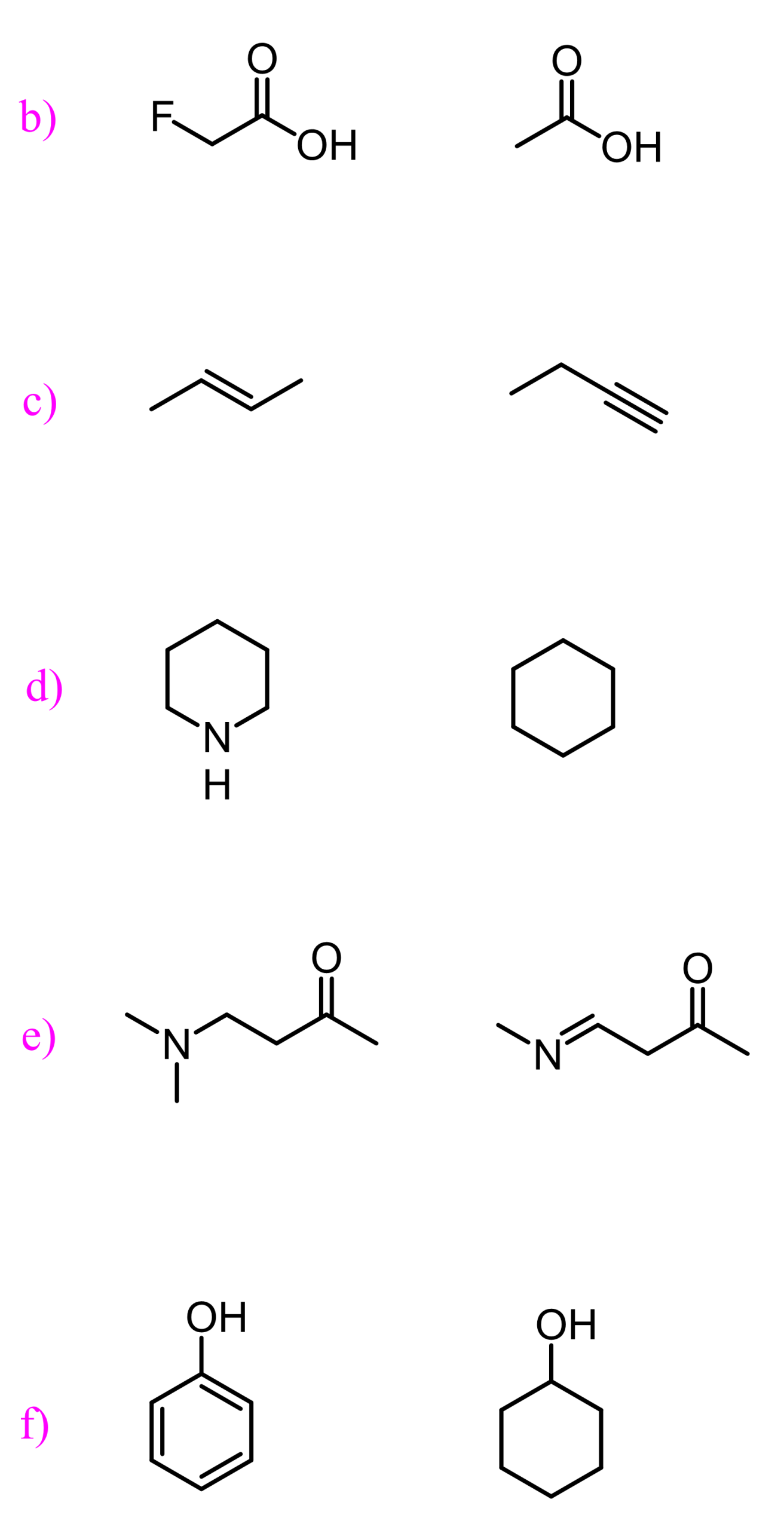
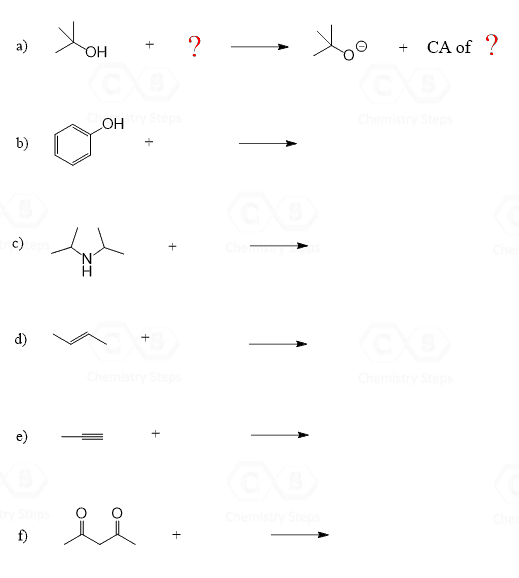
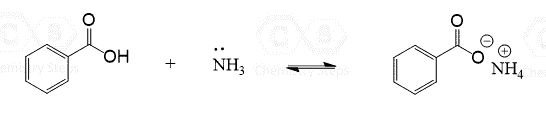This is a summary practice problem set on organic acids and bases. The questions cover:
The definition of organic acids and bases, as well as conjugate acids and bases, drawing acid-base mechanism, acid and base strength based on pKa, factors determining the acid strength, choosing acids and bases for protonating or deprotonating organic compounds, as well as Lewis acids and bases.
The problems are taken from the corresponding topics which, together with the answers, can be found by following the “Answers” link after each problem set.
There is also a multiple-choice quiz on organic acids and bases available for registered users of Chemistry Steps:
Organic Acids and Bases Quiz