To determine the R and S configuration of the chiral carbon atoms in a Fischer projection, we first need to recall the concept of the Fischer projection. And that is, the horizontal groups are pointing towards the viewer (wedge), and the groups on the vertical axis are pointing away from the viewer (dash), even though all the bonds are shown in plain lines.

The rules for determining the absolute configurations are all the same that we learned in an earlier article: How to Determine the R and S configuration
For example, let’s determine the configuration of the chiral carbon in the following Fischer projection:
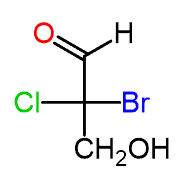
Step 1. Draw the horizontal bonds as wedge lines:
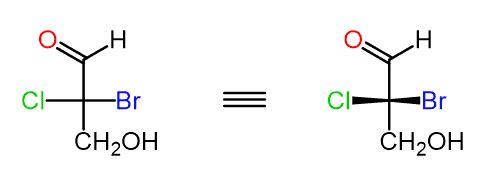
Step 2. Assign the priorities of the four groups:

Notice that the aldehyde group has a higher priority than the alcohol because the C=O double bond is counted as if the carbon is connected to two oxygen atoms.
Step 3. Determine the direction of the arrow; if the lowest priority is pointing away from you (vertical position), then the configuration is as it should be: clockwise (CW)-R, counterclockwise (CCW)-S:

In this case, the CH2OH group is the lowest priority and pointing away from us; therefore, the configuration is based on the direction of the arrow.
Let’s now consider an example where the lowest priority is on a horizontal position (wedge line):
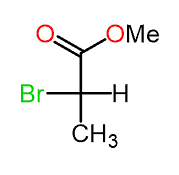
Step 1. Draw the horizontal bonds as wedge lines:
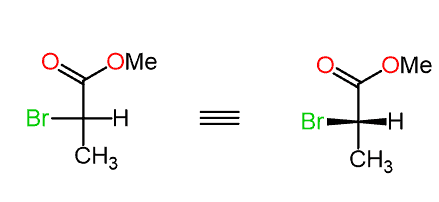
Keep in mind that the lowest priority is pointing towards as.
Step 2. Assign the priorities:

Step 3. Determine the direction, not the arrow, and change the result (R to S or S to R) because the lowest priority is pointing towards as:

Fischer Projections with More Than One Chiral Center
When there is more than one chiral center in the Fischer projection, it gets a little more complicated as they need to be assigned separately.
For example, determine the absolute configuration of each chiral carbon in the following Fischer projection:

Let’s start with the top carbon, treating the second one simply as a priority group for the R and S designation. The methyl group is the lowest priority and therefore, the counterclockwise indicating an S configuration must be switched to R:

And now, we can concentrate on the second carbon atom by treating the first one as a priority group to assign the configuration:

The NH2 group is the highest priority, followed by the carbon connected to Cl, and then the methyl group on the bottom.
The horizontal hydrogen indicates that the chirality should be changed from R to S.
In the end, let’s put all these steps in a little summary for determining the R and S configuration in Fischer projections:

Summarizing R and S Configurations on Fischer Projections
The first thing you need to do when determining R and S on Fischer projections is to remember the stereochemical meaning of the horizontal and vertical groups.
In Fischer projections:
-
Horizontal lines represent bonds pointing toward you (coming out of the plane).
-
Vertical lines represent bonds pointing away from you (going into the plane).
This is important in and of itself, but for R and S specifically, remember: we need to know for certain where the lowest priority group is pointing to assign the configuration correctly.
So when assigning R or S:
-
If the lowest priority group is on a vertical line (pointing away), you can assign the configuration as usual – no adjustment needed.
-
If the lowest priority group is on a horizontal line (pointing toward you), assign R or S normally, but flip the result at the end.

