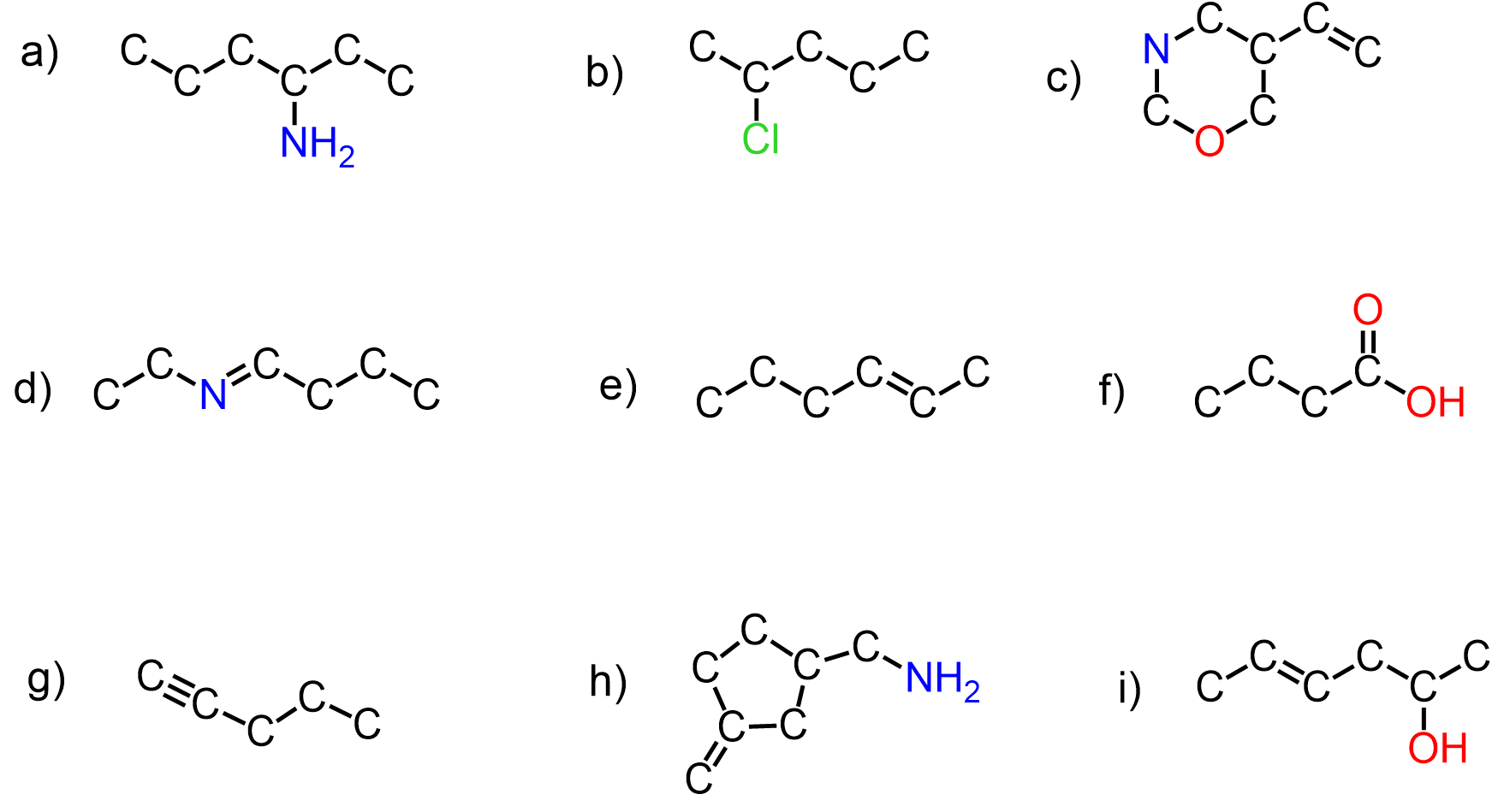
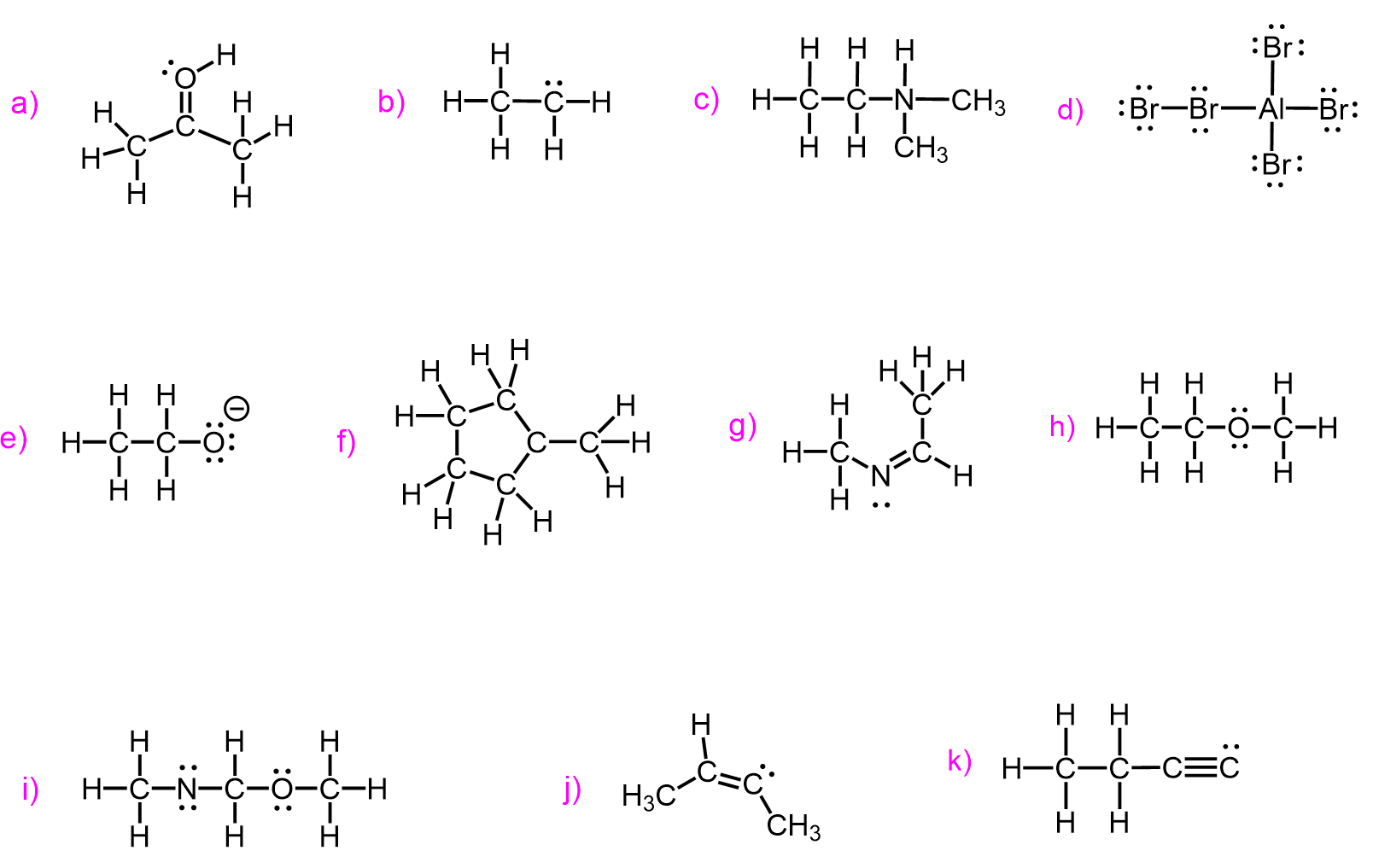
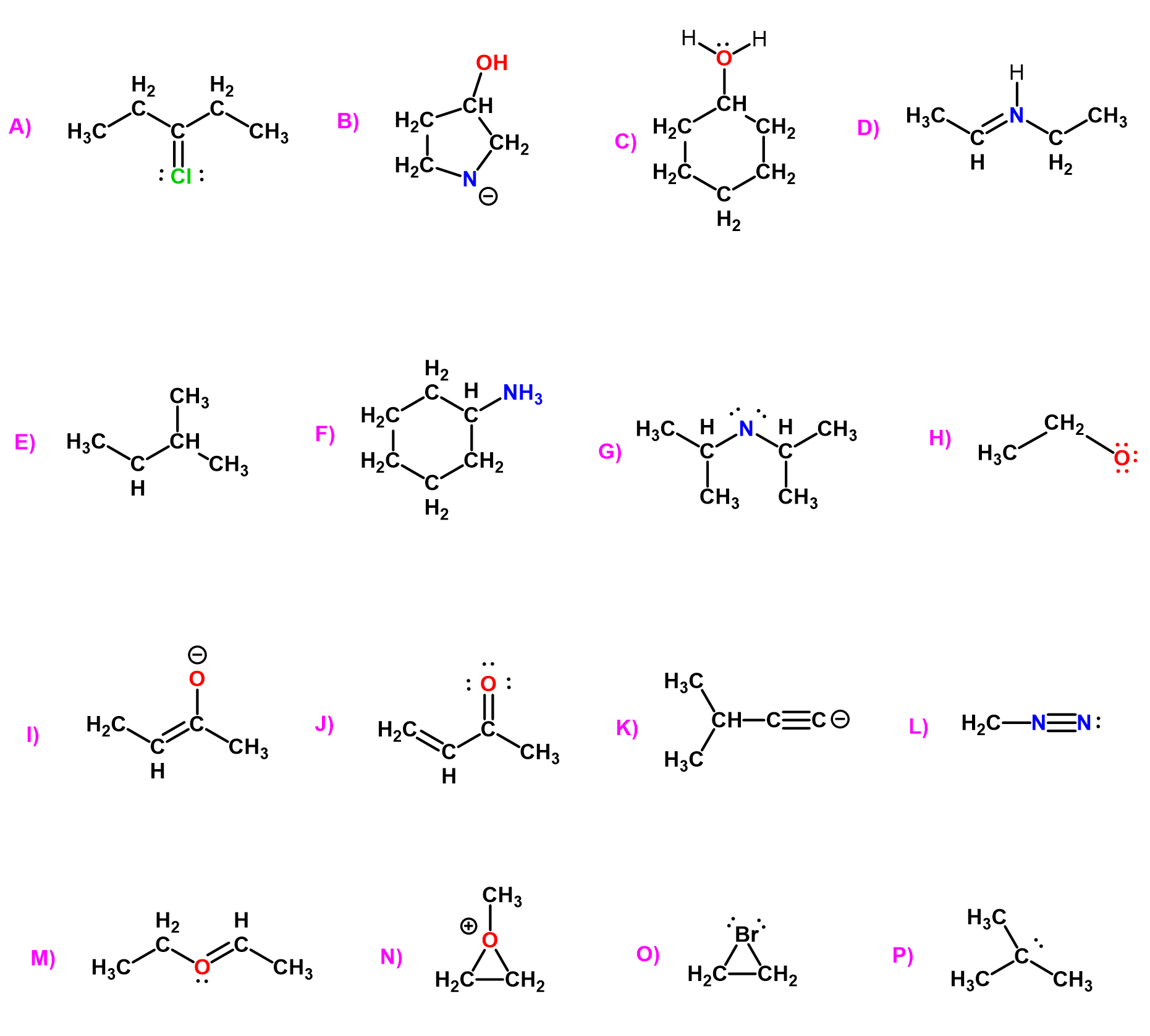
Check the updated version of this post here.
What is Valency?
Before getting to the Formal Charge, let’s recall the valency of elements in organic chemistry. Valency is the tendency of elements to make a certain number of bonds.
Take a look at these molecules and try to find a bonding pattern for each element:
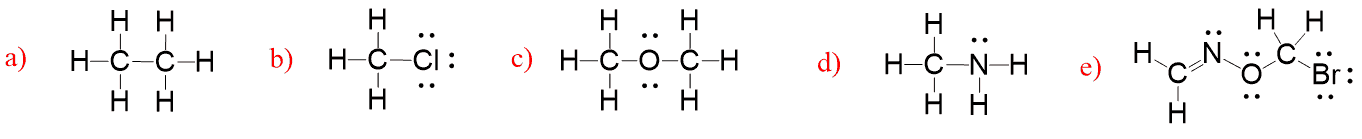
What we notice is that carbon has four bonds in each molecule, oxygen has two, nitrogen–three and halogens, together with hydrogen tend to have only one bond. So this is the valency of those atoms which, in simple words, is the number of bonds the given element forms most often.
This doesn’t mean, for example, that carbon can never have less than four bonds, or the oxygen will never be binding to more than two atoms. However, valency does indicate the number of bonds that every element likes to form. Below is a chart that shows the valency of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, halogens, and hydrogen.
Memorize these numbers! They will help you a lot to save time in drawing proper organic structures and recognizing if a Lewis structure is incorrect/incomplete.
Formal Charges
Formal charges are the quantitative and qualitative indicators of how much the given element deviates from its standard valency. For example, a carbon atom with three bonds is most likely going to be positively charged since it normally has four bonds, and because the bonds are made of electrons, their decrease indicates less negative charge.
In a more mathematical definition, formal charge is the difference between the valence electrons of an atom and how many of electrons it “owns” in that particular Lewis structure.
Remember that the number of valence electrons is determined simply according to the atom’s group number. Therefore, we can easily determine this difference.
For example, the nitrogen below has a formal charge of a negative one. This is because it has five valence electrons, but it owns six – two lone pairs and one electron from each bond:

Notice that the lone pairs are also considered when identifying how many electrons the atom has.
How to Identify and Calculate the Formal Charge
We mentioned above that sometimes Lewis structures may be incorrect or incomplete. This can be because the atoms are not connected correctly or/and the electrons are not distributed as they should be according to the valency of elements.
For example, below is the incomplete Lewis structure of the methoxide ion:
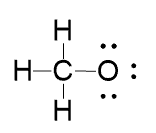
We just mentioned that this structure is an ion, but where is the charge – is it on the carbon, hydrogen, or the oxygen? And what is the charge – is it positive, is it negative?
Now, you don’t want to spend the whole day identifying the formal charge on a structure. Instead, focus on the element(s) that do not follow its valency. In this case, it is the oxygen, as it only has one bond and three lone pairs instead of the 2×2 according to the table.
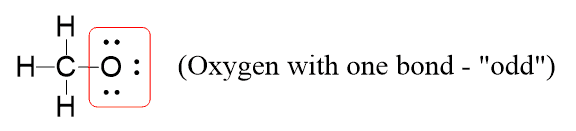
On the other hand, the charge can’t be on the carbon or the hydrogen because they both match their standard valency. or the oxygen but
The formal charge of the oxygen (and in general) can be calculated by this formula:
FC= V – (N + B)
Where:
V – number of valence electrons
N – number of nonbonding electrons
B – number of bonds
So, the formal charge of the oxygen will be
FC (O) = 6 – (6 + 1) = -1
This can also be found in the chart above: oxygen likes to have two bonds with two lone pairs of electrons, and that is when it does not have a formal charge. Keep in mind that in general, atoms do not like to be charged.
In summary, if you need to identify and determine the formal charge, look for a strange atom such as a carbon with three bonds, an oxygen not having two bonds and etc. Once you spot it, use the formula to calculate the formal charge, or alternatively, practice until it becomes natural to your eyes to see the trend for bonds and charges in organic structures.
In the next post, we will talk about the lone pairs and how to determine them based on the formal charge number of bonds.
Check this 60-question, Multiple-Choice Quiz with a 2-hour Video Solution covering Lewis Structures, Resonance structures, Localized and Delocalized Lone Pairs, Bond-line structures, Functional Groups, Formal Charges, Curved Arrows, and Constitutional Isomers.
Molecular Representations Quiz